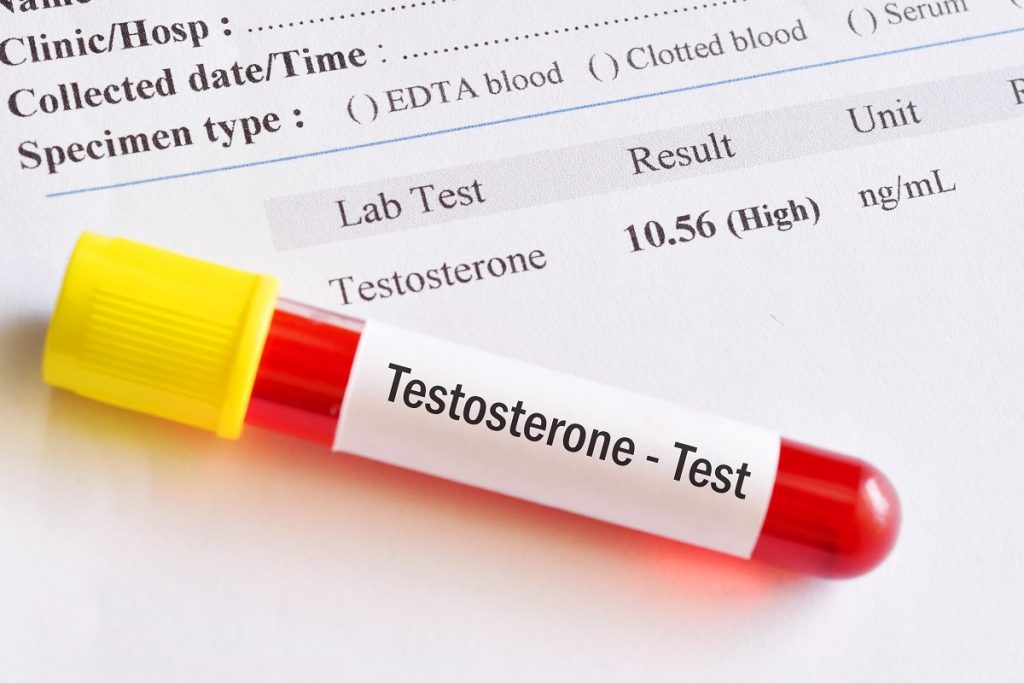
Introduction
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) has become a widely discussed topic, especially among men who may experience symptoms of low testosterone. If you’re considering TRT, you likely have several questions about how to get started and what the process entails. This comprehensive guide will address the top 10 questions asked on search engines and provide detailed answers to help you understand how to obtain TRT.
Section 1: What Is Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)?
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a medically supervised treatment designed to address low testosterone levels in individuals with clinically diagnosed hypogonadism. Hypogonadism refers to a condition in which the testes (or ovaries in women) produce insufficient amounts of testosterone, the primary male sex hormone responsible for various physiological and psychological functions.
Testosterone plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of male sexual characteristics, such as facial hair, deep voice, and muscle mass. Beyond these visible traits, it also has a significant impact on overall health. In both men and women, testosterone influences bone density, fat distribution, red blood cell production, and sex drive.
When testosterone levels drop below the normal range, individuals may experience a wide range of symptoms that can affect their quality of life. Some of the common signs of low testosterone include:
- Fatigue: Individuals with low testosterone often report feeling consistently tired and lacking energy.
- Low Libido: A decrease in sex drive is a common symptom, leading to reduced sexual desire and function.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Men with low testosterone may experience difficulties in achieving and maintaining erections.
- Mood Changes: Low testosterone levels have been associated with mood swings, irritability, and even depression.
- Muscle Loss: Testosterone contributes to muscle development, and its decline can lead to muscle weakness and decreased muscle mass.
- Increased Body Fat: Low testosterone is linked to an increase in body fat, particularly around the abdomen.
- Cognitive Impairment: Some individuals with low testosterone may experience difficulties with memory and concentration.
- Reduced Bone Density: Testosterone plays a role in maintaining bone density, so low levels can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
It’s important to note that experiencing one or more of these symptoms doesn’t necessarily mean you have low testosterone. To determine if you have low testosterone, a blood test is essential. Your healthcare provider will measure your total testosterone levels, ideally in the morning when levels are at their highest.
The typical range for total testosterone levels in adult men is between 270 to 1070 ng/dL (nanograms per deciliter), though this range can vary depending on the laboratory. If your test results consistently show levels below the lower limit of the normal range and you are experiencing the aforementioned symptoms, you may be a candidate for TRT.
TRT aims to restore testosterone levels to within the normal range, alleviating the associated symptoms and improving overall quality of life. It’s important to emphasize that TRT is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and its success depends on individual factors such as the cause of low testosterone, age, and overall health.
Before starting TRT, it’s crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare provider who specializes in hormone therapy. They will assess your medical history, conduct a physical examination, and order necessary blood tests to determine if TRT is the right treatment for you. Once you and your healthcare provider decide to proceed with TRT, they will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan that includes choosing the most suitable method of administration and monitoring your progress to ensure optimal results.
Section 2: Who Needs TRT?
Determining whether you need Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a critical step that requires a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified healthcare provider. Not everyone with low testosterone levels will benefit from TRT, as individual circumstances, health factors, and symptoms play a significant role in this decision-making process.
Low testosterone, or hypogonadism, can manifest in various ways, and it’s essential to recognize the symptoms that may indicate a need for TRT. Here’s a closer look at who may benefit from TRT:
- Clinically Diagnosed Low Testosterone Levels: The primary criterion for TRT eligibility is a clinical diagnosis of low testosterone. This diagnosis is established through blood tests that measure your total testosterone levels. Generally, a total testosterone level below 300 ng/dL (nanograms per deciliter) is considered low. However, the specific range may vary depending on the laboratory and your age.
- Symptoms of Low Testosterone: In addition to low testosterone levels, experiencing symptoms associated with low testosterone is a crucial factor in determining the need for TRT. These symptoms can significantly impact your quality of life and may include:
- Fatigue: Persistent fatigue and low energy levels.
- Low Libido: Reduced sexual desire and problems with sexual function.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Difficulty achieving and maintaining erections (in men).
- Mood Changes: Mood swings, irritability, or feelings of depression.
- Muscle Loss: Decreased muscle mass and strength.
- Increased Body Fat: Accumulation of body fat, particularly around the abdomen.
- Cognitive Issues: Problems with memory, concentration, and cognitive function.
- Reduced Bone Density: Increased risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
If you are experiencing one or more of these symptoms and your blood tests reveal consistently low testosterone levels, it may be an indication that TRT could benefit you.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions or treatments can lead to low testosterone levels. For example, conditions like Klinefelter syndrome, pituitary gland disorders, and some genetic disorders can affect testosterone production. Additionally, individuals undergoing cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, may experience a decline in testosterone levels. In such cases, TRT may be considered as a therapeutic option to address the effects of these conditions or treatments.
It’s important to emphasize that the decision to pursue TRT should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider who specializes in hormone therapy. TRT is a medical treatment, and its success depends on various factors, including the underlying cause of low testosterone, age, overall health, and individual preferences.
Before initiating TRT, you and your healthcare provider will engage in a thorough discussion to assess the potential benefits and risks associated with the treatment. This conversation will help you make an informed decision about whether TRT is the right approach for addressing your low testosterone levels and associated symptoms.
Furthermore, it’s essential to consider alternative treatments and lifestyle modifications that may help improve testosterone levels naturally. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on these options, which may include dietary changes, exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep.
In conclusion, TRT is a valuable therapeutic option for individuals with clinically diagnosed low testosterone levels who are experiencing symptoms that negatively impact their well-being. The decision to pursue TRT should be based on a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified healthcare provider and a thorough discussion of the potential benefits, risks, and alternatives. Ultimately, the goal of TRT is to improve the quality of life and overall health of individuals with low testosterone.
Section 3: How Do You Know If You Have Low Testosterone?
Determining whether you have low testosterone is a crucial first step in considering Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT). Symptoms associated with low testosterone can vary widely among individuals and may overlap with other health issues, making an accurate diagnosis essential. To establish whether low testosterone is a concern, a series of steps and assessments are typically undertaken:
- Recognizing Symptoms: The first indication that you may have low testosterone is the presence of symptoms. As mentioned in the previous section, common symptoms include fatigue, low libido, erectile dysfunction (in men), mood swings, muscle loss, increased body fat, cognitive difficulties, and reduced bone density. If you are experiencing some or several of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
- Consulting a Healthcare Provider: If you suspect low testosterone or experience symptoms associated with it, the next step is to schedule an appointment with a healthcare provider. This could be your primary care physician, an endocrinologist, a urologist, or a specialist in hormone therapy.
- Medical History Review: During your appointment, your healthcare provider will conduct a detailed review of your medical history. They will ask questions about your symptoms, when they started, their severity, and any other relevant medical information. It’s essential to be open and honest during this discussion to provide your healthcare provider with a clear picture of your health.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination is often performed to assess your overall health and identify any visible signs or conditions that may be related to low testosterone. This examination may include checking for signs such as gynecomastia (breast enlargement in men) and changes in body hair distribution.
- Blood Tests: The most definitive method for diagnosing low testosterone involves blood tests. Your healthcare provider will order a series of blood tests to measure your testosterone levels. These tests usually include:
- Total Testosterone: This measures the overall amount of testosterone in your bloodstream.
- Free Testosterone: This measures the amount of testosterone that is not bound to proteins and is available for use by your body.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): These hormones help regulate testosterone production, and their levels can provide additional insights into the cause of low testosterone.
These blood tests are typically conducted in the morning when testosterone levels are naturally at their highest.
- Interpreting Test Results: Once the blood test results are available, your healthcare provider will interpret them in the context of your symptoms and medical history. It’s important to note that testosterone levels can vary throughout the day and even from one day to the next, so multiple tests may be necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
- Determining Clinical Need: If your blood test results consistently show total testosterone levels below the lower limit of the normal range (typically below 300 ng/dL), and you are experiencing symptoms associated with low testosterone, your healthcare provider may diagnose you with hypogonadism and consider TRT as a treatment option.
It’s crucial to approach the diagnosis of low testosterone with patience and a collaborative mindset. TRT is a significant medical intervention, and a clear diagnosis is essential to ensure it’s the most appropriate course of action for your specific situation.
Recognizing and diagnosing low testosterone involves a multifaceted approach, including recognizing symptoms, consulting a healthcare provider, reviewing medical history, conducting a physical examination, and undergoing blood tests. A comprehensive evaluation by a qualified healthcare provider is essential for making an accurate diagnosis and determining the most suitable treatment, which may include Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) if clinically indicated. Remember that TRT should only be pursued after careful consideration and consultation with a healthcare professional.
Section 4: Finding a Healthcare Provider
Once you’ve determined that you may benefit from Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) based on symptoms and a low testosterone diagnosis, the next crucial step is to find a healthcare provider who specializes in hormone therapy. This provider will guide you through the TRT process, ensuring that you receive the appropriate care and treatment tailored to your needs.
Here are the steps to help you find the right healthcare provider for your TRT journey:
- Primary Care Physician: Start by discussing your concerns with your primary care physician. They are often the first point of contact for healthcare needs. Your primary care physician can assess your symptoms, order initial blood tests, and provide valuable insights. If necessary, they can refer you to a specialist for further evaluation and treatment.
- Endocrinologist: An endocrinologist is a specialist in hormone-related disorders, making them a particularly relevant choice for evaluating and managing low testosterone. If your primary care physician suspects hormone imbalances or complex cases, they may refer you to an endocrinologist.
- Urologist: Urologists specialize in the urinary tract and male reproductive organs, making them well-suited to address issues related to low testosterone. They often have experience in diagnosing and treating conditions like erectile dysfunction and may offer TRT consultations.
- Hormone Clinics: Some clinics specialize in hormone replacement therapy, including TRT. These specialized facilities are equipped to evaluate and treat hormone-related issues, providing comprehensive care tailored to your specific needs. Research local hormone clinics and consult with them regarding your options.
When searching for a healthcare provider, consider the following factors to ensure you make an informed choice:
- Experience: Look for providers with extensive experience in hormone therapy and TRT. Experienced providers are better equipped to evaluate your condition accurately and develop effective treatment plans.
- Qualifications: Verify the qualifications and credentials of potential healthcare providers. Ensure they are licensed and board-certified in their respective specialties.
- Patient Reviews: Check online reviews and seek recommendations from friends, family, or support groups if available. Hearing about others’ experiences can help you gauge the quality of care provided.
- Accessibility: Consider the location of the healthcare provider’s practice and their availability for appointments. Convenient access to care is essential for ongoing TRT management.
- Communication: A strong patient-provider relationship is vital for successful TRT. Choose a healthcare provider who communicates openly, listens to your concerns, and involves you in the decision-making process.
- Insurance Coverage: Verify whether the healthcare provider accepts your health insurance, as this can significantly impact the cost of your TRT treatment.
Once you’ve selected a healthcare provider, schedule an initial consultation to discuss your symptoms, medical history, and the results of any previous tests. During this appointment, your provider will conduct a comprehensive evaluation to determine whether TRT is a suitable treatment option for you.
It’s essential to be open and honest during this consultation, as it will help your provider make an accurate diagnosis and create a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs. If TRT is recommended, your provider will guide you through the next steps, which may include additional testing, treatment options, and ongoing monitoring.
Finding the right healthcare provider for Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a critical step in your journey to address low testosterone. Consider the qualifications, experience, patient reviews, and accessibility of potential providers before making your choice. Establishing a strong patient-provider relationship is essential for successful TRT management, ensuring that you receive the most appropriate and effective treatment for your specific condition.
Section 5: Initial Consultation
The initial consultation with a healthcare provider is a pivotal moment in the journey towards Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT). During this appointment, you will have the opportunity to discuss your symptoms, medical history, and the results of any previous tests. This consultation serves as the foundation for evaluating whether TRT is a suitable treatment option for your specific circumstances.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of what to expect during the initial consultation:
- Medical History Review: Your healthcare provider will begin by taking a comprehensive medical history. This includes discussing your current symptoms, their duration, severity, and any factors that may exacerbate or alleviate them. Be prepared to provide details about your overall health, past medical conditions, surgeries, and any medications or supplements you are currently taking. This information helps your provider understand your medical background and potential contributing factors to your low testosterone.
- Symptom Assessment: Your provider will delve into the specific symptoms you’ve been experiencing due to low testosterone. Common symptoms include fatigue, low libido, erectile dysfunction (in men), mood swings, muscle loss, increased body fat, cognitive difficulties, and reduced bone density. Describing the impact of these symptoms on your daily life and well-being is essential for your provider to gauge their severity.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination may be conducted to assess your overall health and identify any visible signs or conditions that may be related to low testosterone. Your provider may check for signs such as gynecomastia (breast enlargement in men) or changes in body hair distribution. The physical examination helps to confirm the clinical picture and guide further evaluation.
- Blood Tests: If you haven’t already undergone blood tests to measure your testosterone levels, your provider may order these tests during the initial consultation. Blood tests are a fundamental aspect of diagnosing low testosterone, and the results will provide valuable data to support the decision-making process.
- Discussion of Symptoms and Concerns: The consultation provides you with an opportunity to openly discuss your symptoms and express any concerns or questions you may have. It’s crucial to communicate effectively with your healthcare provider to ensure that all relevant information is considered in your diagnosis and treatment plan.
- Treatment Options and Expectations: If your healthcare provider suspects that low testosterone is contributing to your symptoms and the blood test results confirm this, they will discuss treatment options, including TRT. Your provider will explain the potential benefits of TRT, such as improved energy, mood, and sexual function, as well as the potential risks and side effects. This discussion is an essential part of informed decision-making, allowing you to weigh the benefits and potential drawbacks of TRT.
- Developing a Treatment Plan: If both you and your provider agree that TRT is an appropriate course of action, the next step is to develop a personalized treatment plan. This plan will outline the specific details of your TRT, including the method of administration, dosage, and frequency. Your provider will consider your preferences and medical history when determining the most suitable treatment approach.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: Your healthcare provider will explain the importance of regular monitoring during your TRT journey. Regular follow-up appointments and blood tests will be scheduled to assess your progress, make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan, and address any concerns or side effects that may arise.
Remember that the initial consultation is a collaborative process between you and your healthcare provider. It is an opportunity to gather information, ask questions, and make informed decisions about your health and treatment options. Open and honest communication with your provider is key to ensuring that your TRT experience is safe, effective, and tailored to your unique needs.
The initial consultation with a healthcare provider is a crucial step in the TRT journey. It involves a comprehensive review of your medical history, an assessment of your symptoms, physical examination, blood tests, and a discussion of treatment options and expectations. This consultation sets the stage for personalized TRT treatment, ensuring that you receive the most appropriate care to address your low testosterone and improve your overall quality of life.
Section 6: The TRT Decision
The decision to embark on Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a significant step and should be approached with careful consideration and collaboration between you and your healthcare provider. TRT is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and its appropriateness depends on various factors, including your clinical condition, symptoms, and overall health. This section explores the key elements of the TRT decision-making process:
Benefits vs. Risks Assessment: One of the primary objectives of the TRT decision is to weigh the potential benefits against the associated risks. Your healthcare provider will discuss the expected benefits, which may include improved energy levels, mood, sexual function, muscle mass, and cognitive function. However, it’s essential to recognize that TRT is not without risks. Possible side effects and risks of TRT may include acne, mood swings, fluid retention, increased red blood cell count, and gynecomastia (breast enlargement in men). Your provider will outline these potential risks during your consultation.
Individualized Treatment Plan: TRT is not a one-size-fits-all treatment. Your healthcare provider will work with you to develop an individualized treatment plan tailored to your unique needs and preferences. This plan will outline the specific details of your TRT, including the method of administration (such as injections, gels, patches, or implants), dosage, and frequency of treatment. It’s crucial to collaborate with your provider to ensure that your treatment plan aligns with your lifestyle and comfort level.
Monitoring and Follow-Up: TRT is an ongoing treatment that requires regular monitoring and follow-up appointments. Your provider will schedule these appointments to assess your progress, check for any potential side effects, and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. Monitoring ensures that your TRT remains safe and effective over time.
Treatment Duration: TRT may be a long-term treatment. Your provider will discuss the expected duration of treatment, which can vary from several months to years, depending on your clinical condition and individual response to therapy. The goal of TRT is to maintain testosterone levels within the normal range, alleviate symptoms, and improve your overall quality of life.
Costs and Insurance: It’s essential to discuss the financial aspects of TRT with your healthcare provider. TRT costs can vary depending on the method of administration, medication, and frequency of treatment. Additionally, insurance coverage for TRT may vary, so it’s advisable to inquire about your specific insurance plan’s coverage for hormone replacement therapy.
Alternative Treatment Options: In some cases, alternative treatments or lifestyle modifications may be considered before or alongside TRT. These alternatives may include dietary changes, exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on these options and help you determine whether they are suitable for your situation.
Decision-Making Collaboration: Ultimately, the decision to pursue TRT should be a collaborative one between you and your healthcare provider. Your provider will provide you with all the necessary information about the potential benefits and risks of TRT, as well as alternative treatment options. Tey will answer your questions and address any concerns you may have, empowering you to make an informed decision that aligns with your health goals and values.
Informed Consent: Once you’ve discussed the benefits, risks, and treatment plan with your healthcare provider and have decided to move forward with TRT, you will likely be asked to provide informed consent. Informed consent acknowledges that you understand the treatment, its potential outcomes, and any associated risks. It demonstrates your willingness to proceed with TRT under the guidance of your healthcare provider.
Continued Communication: Effective communication with your healthcare provider is critical throughout your TRT journey. You should feel comfortable discussing any changes in symptoms, side effects, or concerns that arise during treatment. This ongoing dialogue ensures that your treatment plan remains tailored to your evolving needs and that any issues are addressed promptly.
The decision to pursue Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a collaborative process between you and your healthcare provider. It involves a thorough assessment of the potential benefits and risks, the development of an individualized treatment plan, and ongoing monitoring to ensure the safety and effectiveness of TRT. By actively engaging in this decision-making process and maintaining open communication with your provider, you can make informed choices that support your overall well-being and quality of life. Remember that your healthcare provider is your trusted partner in optimizing your hormone health and addressing the symptoms associated with low testosterone.
Section 7: Starting TRT
Initiating Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) marks a significant step in addressing low testosterone levels and associated symptoms. Once you and your healthcare provider have carefully evaluated your condition, discussed the benefits and risks, and developed a personalized treatment plan, you can begin your TRT journey. In this section, we delve into the practical aspects of starting TRT:
Prescription and Medication Selection: Your healthcare provider will prescribe the specific testosterone replacement medication that aligns with your treatment plan. TRT medications are available in various forms, including:
- Intramuscular Injections: These injections are administered into the muscle, typically in the buttocks or thigh, every one to two weeks.
- Transdermal Gels: Gels are applied topically to the skin, often on the shoulders, upper arms, or abdomen, daily.
- Transdermal Patches: Patches are placed on clean, dry skin and are usually replaced daily or as directed.
- Implants: Testosterone implants are surgically inserted under the skin and release a steady dose over several months.
Your healthcare provider will guide you in selecting the most appropriate form of TRT based on your medical history, preferences, and treatment goals.
Instructions and Administration: Once you have your prescribed medication, your healthcare provider will provide detailed instructions on how to properly administer or apply it. It’s crucial to follow these instructions meticulously to ensure the effectiveness of your TRT. If you have any questions or uncertainties about the administration process, do not hesitate to seek clarification from your provider.
Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular monitoring is an integral part of TRT. Your provider will schedule follow-up appointments to assess your progress, monitor your testosterone levels, and evaluate how well you are responding to treatment. During these appointments, you will have the opportunity to discuss any changes in symptoms, side effects, or concerns related to your TRT. Your provider may make adjustments to your treatment plan if necessary.
Adherence to Treatment: Adherence to your prescribed TRT regimen is vital for achieving the desired results. Consistently following the recommended schedule for medication administration, attending follow-up appointments, and communicating openly with your healthcare provider are essential components of successful TRT. Non-adherence can impact treatment effectiveness and overall outcomes.
Side Effects and Their Management: While TRT can be highly beneficial, it may also entail side effects. Common side effects include acne, mood swings, fluid retention, increased red blood cell count, and gynecomastia (breast enlargement in men). If you experience any of these side effects or others that concern you, it’s essential to promptly communicate with your healthcare provider. They can provide guidance on managing side effects and may adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
Treatment Duration: TRT is often considered a long-term treatment, and the duration can vary from several months to years, depending on your specific condition and response to therapy. Your healthcare provider will discuss the expected duration of your TRT during your initial consultation and follow-up appointments.
Lifestyle and Health Considerations: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can complement the effectiveness of TRT. Engaging in regular physical activity, following a balanced diet, managing stress, getting adequate sleep, and refraining from smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are all factors that can support your overall well-being and optimize the benefits of TRT.
Costs and Insurance: The financial aspects of TRT should be discussed with your healthcare provider, as well as with your insurance provider. TRT costs can vary depending on the chosen method of administration and the specific medication. Understanding your insurance coverage and any out-of-pocket expenses is essential to budgeting for your TRT treatment.
Starting Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a structured process that involves obtaining the prescribed medication, diligently adhering to treatment guidelines, and actively participating in the monitoring and follow-up schedule set by your healthcare provider. TRT is a personalized treatment that requires ongoing collaboration between you and your provider to ensure its safety and effectiveness. By adhering to your treatment plan, maintaining open communication, and addressing any concerns or side effects promptly, you can maximize the benefits of TRT and work towards achieving your health and well-being goals. Remember that your healthcare provider is your partner in this journey, committed to helping you address low testosterone and improve your quality of life.
Section 8: Benefits and Potential Risks of TRT
Understanding the potential benefits and risks of Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is crucial for anyone considering this treatment. TRT can be a highly effective solution for individuals with clinically diagnosed low testosterone levels and associated symptoms, but it’s essential to weigh its advantages against potential drawbacks. In this section, we explore the key benefits and potential risks associated with TRT:
Benefits of TRT:
- Symptom Relief: TRT is primarily prescribed to alleviate the symptoms of low testosterone, which can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Many individuals experience improvements in energy levels, mood, and overall well-being as their testosterone levels are restored to within the normal range.
- Enhanced Libido and Sexual Function: Low libido and sexual dysfunction are common symptoms of low testosterone. TRT can help improve sexual desire, erectile function (in men), and overall sexual satisfaction.
- Increased Muscle Mass and Strength: Testosterone plays a pivotal role in muscle development. TRT can help individuals regain muscle mass and strength, making it easier to engage in physical activities and maintain a healthy body composition.
- Improved Cognitive Function: Some individuals with low testosterone report difficulties with memory, concentration, and cognitive function. TRT may enhance cognitive abilities and mental clarity.
- Reduction in Fatigue: Fatigue is a prevalent symptom of low testosterone. TRT can help combat persistent tiredness, allowing individuals to engage in daily activities with increased vigor and vitality.
- Bone Health: Testosterone contributes to bone density. TRT can help maintain or improve bone health, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
- Enhanced Mood: Low testosterone levels are associated with mood swings, irritability, and even depression. TRT can lead to mood stabilization and an overall sense of well-being.
Potential Risks and Considerations:
- Side Effects: TRT may entail side effects, which can vary among individuals. Common side effects include acne, mood swings, fluid retention, and increased red blood cell count. Gynecomastia (breast enlargement in men) is another possible side effect. Monitoring and communication with your healthcare provider are essential to manage side effects effectively.
- Long-Term Commitment: TRT is often a long-term treatment, and discontinuing it abruptly can lead to a drop in testosterone levels and a return of symptoms. The decision to stop TRT should be made in consultation with your healthcare provider, who can guide you through a safe and gradual cessation if needed.
- Cardiovascular Risks: Some studies have suggested a potential link between TRT and an increased risk of cardiovascular issues, such as heart attack and stroke. However, the evidence is not conclusive, and the cardiovascular risks associated with TRT are still being studied. Your healthcare provider will consider your individual cardiovascular risk factors when prescribing TRT.
- Prostate Health: TRT may cause an enlargement of the prostate gland, which can affect urinary function. Regular prostate monitoring is essential during TRT to detect any abnormalities early.
- Polycythemia: TRT can lead to an increase in red blood cell count, a condition known as polycythemia. Regular blood tests will monitor this risk, and adjustments to your treatment plan may be necessary.
- Infertility: TRT can suppress sperm production, potentially leading to infertility. If fertility preservation is a concern, discuss it with your healthcare provider before starting TRT.
- Costs and Insurance: TRT costs can vary, and insurance coverage may vary as well. It’s important to discuss the financial aspects of TRT with your healthcare provider and verify your insurance coverage.
- Alternative Treatments: Before starting TRT, consider alternative treatments and lifestyle modifications that may help improve testosterone levels naturally. These can include dietary changes, exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) offers several potential benefits for individuals with clinically diagnosed low testosterone levels and associated symptoms. These benefits can include symptom relief, improved libido, increased muscle mass, enhanced cognitive function, and more. However, it’s crucial to be aware of potential risks and side effects associated with TRT, such as acne, mood swings, and cardiovascular considerations. Effective communication with your healthcare provider, regular monitoring, and a thorough understanding of the treatment’s benefits and potential drawbacks will help you make informed decisions about TRT and its role in your overall well-being. Your healthcare provider will work with you to optimize your TRT experience and ensure that the benefits outweigh any potential risks for your specific situation.
Section 9: TRT and Lifestyle
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a valuable medical intervention for individuals with clinically diagnosed low testosterone levels. While TRT can be highly effective in alleviating symptoms and improving overall well-being, it should not be viewed in isolation. The synergy between TRT and a healthy lifestyle can enhance its benefits and promote long-term well-being. In this section, we explore how lifestyle factors can complement TRT and contribute to a more holistic approach to hormone health:
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise is a cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle and can complement the effects of TRT. Engaging in both cardiovascular and strength-training exercises can help optimize muscle growth, reduce body fat, and improve overall physical fitness. Exercise also has mood-enhancing effects, which can synergize with TRT’s mood-stabilizing properties. Before starting or modifying an exercise routine, consult with your healthcare provider to ensure that it aligns with your health goals and TRT plan.
- Nutrition: Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet is essential for overall health and can support the effectiveness of TRT. Adequate intake of essential nutrients, including zinc and vitamin D, is important for testosterone production. A diet rich in lean protein, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can contribute to better overall health. Discuss your dietary goals and any specific nutritional considerations with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact hormone balance, including testosterone levels. Implementing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies can help mitigate stress’s adverse effects. Managing stress can contribute to improved mood and well-being, which can complement TRT’s mood-enhancing benefits.
- Sleep Quality: Quality sleep is vital for hormone production and overall health. Aim for seven to nine hours of uninterrupted sleep each night. Poor sleep can disrupt hormone regulation and may hinder the benefits of TRT. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment are essential for promoting restorative sleep.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking is associated with lower testosterone levels and can have detrimental effects on cardiovascular health. If you smoke, quitting can be a crucial step in optimizing the benefits of TRT and improving your overall health. Seek support and resources to help you quit smoking, as it can be a challenging but highly rewarding endeavor.
- Alcohol Moderation: Excessive alcohol consumption can impact testosterone levels and overall health negatively. If you consume alcohol, do so in moderation. Limiting alcohol intake can support the effectiveness of TRT and promote better overall well-being.
- Regular Check-Ups: Maintaining regular check-ups with your healthcare provider is essential when undergoing TRT. These appointments allow for the monitoring of your testosterone levels, assessment of treatment efficacy, and adjustment of your treatment plan if necessary. Open communication with your provider about lifestyle factors, side effects, and any concerns is vital to ensure that your TRT experience is safe and effective.
- Alternative Therapies: Consider complementary therapies that may further enhance the benefits of TRT. These can include acupuncture, herbal supplements, and biofeedback. Always consult with your healthcare provider before incorporating alternative therapies into your TRT regimen to ensure they align with your treatment plan and overall health goals.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) can be an effective solution for individuals with low testosterone levels and associated symptoms. However, its success can be optimized when combined with a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, stress management, quality sleep, and avoidance of smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. These lifestyle factors not only complement the benefits of TRT but also contribute to your overall well-being and long-term health. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on integrating these lifestyle changes into your TRT journey, tailoring your approach to meet your specific needs and health goals. By embracing a holistic approach to hormone health, you can maximize the benefits of TRT and lead a more fulfilling and healthy life
Section 10: Questions and Answers
Let’s address the 10 most frequently asked questions about how to get Testosterone Replacement Therapy:
Q1: How long does it take to see results from TRT? A1: The time it takes to see results from TRT can vary from person to person. Some individuals may notice improvements in energy, mood, and libido within a few weeks, while others may take several months. It’s essential to follow your provider’s recommendations and attend regular check-ups for optimal results.
Q2: Can TRT be done at home, or does it require clinic visits? A2: TRT can be administered at home, depending on the method prescribed by your healthcare provider. Injections, gels, and patches can typically be self-administered, while implants may require a clinic visit for insertion.
Q3: Is TRT safe for long-term use? A3: TRT can be safe for long-term use when monitored by a qualified healthcare provider. Regular check-ups and adjustments to your treatment plan, if necessary, can help mitigate potential risks.
Q4: Are there age restrictions for TRT? A4: There is no specific age limit for TRT. The decision to undergo TRT should be based on clinical need and individual circumstances rather than age alone. Your healthcare provider will evaluate your eligibility.
Q5: Can TRT help with infertility? A5: TRT may not be the best option for individuals looking to improve fertility. In fact, TRT can suppress sperm production. If fertility is a concern, discuss alternative treatments with your healthcare provider.
Q6: Are there natural alternatives to TRT? A6: Yes, lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet, exercise, and stress management, can help naturally boost testosterone levels in some cases. However, these methods may not be as effective for individuals with clinically low testosterone.
Q7: What are the costs of TRT, and does insurance cover it? A7: The cost of TRT varies depending on the method and the medication prescribed. Insurance coverage also varies. Check with your healthcare provider and insurance company to understand the costs and coverage for your specific treatment plan.
Q8: Are there any dietary restrictions while on TRT? A8: There are typically no specific dietary restrictions while on TRT. However, maintaining a balanced diet with sufficient nutrients, especially zinc and vitamin D, can support the effectiveness of TRT.
Q9: Can TRT interact with other medications or medical conditions? A9: TRT can interact with certain medications and medical conditions. Inform your healthcare provider about all medications and medical conditions you have to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Q10: Can I stop TRT once I start it? A10: The decision to stop TRT should be made in consultation with your healthcare provider. Abruptly discontinuing TRT can lead to a drop in testosterone levels and a return of symptoms. Your provider can guide you through a safe and gradual cessation if needed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, embarking on Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) represents a significant step for individuals grappling with low testosterone levels and the associated symptoms that can profoundly affect their quality of life. Throughout this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the various facets of TRT, from recognizing the signs of low testosterone to making informed decisions and incorporating a holistic approach to hormone health. It’s important to emphasize several key takeaways as we wrap up our discussion on TRT:
- Informed Decision-Making: The decision to pursue TRT should be a well-informed and collaborative one. Engage in open and honest discussions with your healthcare provider, ask questions, and express your concerns. This partnership ensures that you are actively involved in your treatment plan, making choices that align with your health goals and values.
- Individualized Treatment: TRT is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Each person’s experience with low testosterone is unique, and TRT should be tailored to your specific needs and preferences. Work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that optimizes the benefits of TRT while addressing your specific concerns.
- Monitoring and Communication: Regular monitoring and communication with your healthcare provider are essential components of a successful TRT journey. Follow-up appointments, blood tests, and ongoing discussions help ensure that your treatment remains safe and effective. Promptly share any changes in symptoms, side effects, or concerns with your provider.
- Lifestyle Synergy: TRT is most effective when combined with a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, stress management, quality sleep, and the avoidance of smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. These lifestyle factors not only enhance the benefits of TRT but also contribute to your overall well-being.
- Holistic Approach: Recognize that TRT is just one aspect of your health journey. Consider complementary therapies, alternative treatments, and lifestyle modifications that may further support your hormone health and well-being. Consult with your healthcare provider to integrate these approaches effectively.
- Long-Term Commitment: TRT is often a long-term treatment, and adherence to your prescribed regimen is vital for success. Understand that discontinuing TRT abruptly can lead to a return of symptoms, so decisions to stop treatment should be made in consultation with your provider.
- Continual Learning: Stay informed about developments in hormone therapy and research related to TRT. Knowledge is empowering, and ongoing education can help you make informed choices and actively participate in your health journey.
By approaching TRT with these principles in mind, you can navigate your treatment journey with confidence and optimize the benefits of TRT while maintaining a holistic perspective on your overall health and well-being. Remember that your healthcare provider is your trusted partner in this journey, dedicated to helping you achieve hormone balance, alleviate symptoms, and improve your quality of life. Through informed decisions, a personalized treatment plan, and a commitment to a healthy lifestyle, you can embark on a fulfilling path towards hormone health and overall well-being.