How Testosterone Replacement Therapy Can Lead to Gyno (and What to Do About It)
Introduction: Understanding TRT and Gynecomastia
Testosterone Replacement Therapy, often referred to as TRT, is a medical treatment used to address low levels of testosterone in men. Testosterone is a critical hormone in the male body, playing a vital role in maintaining muscle mass, bone density, libido, mood, and overall energy levels. When testosterone levels drop below normal due to aging, medical conditions, or other factors, men may experience symptoms such as fatigue, reduced sex drive, difficulty concentrating, and even depression. TRT aims to restore testosterone levels to a healthy range, helping alleviate these symptoms and improve quality of life.
While TRT can be highly effective for managing low testosterone, it is not without risks. One potential side effect of TRT is gynecomastia, often called “gyno.” Gynecomastia is the abnormal enlargement of breast tissue in males, which can be both physically uncomfortable and emotionally distressing. It is important to understand how gynecomastia occurs and why it can be linked to testosterone replacement therapy.
To grasp the connection between TRT and gynecomastia, it is helpful to understand the basic hormonal processes in the male body. Testosterone and estrogen are two key hormones that play different roles. Testosterone is typically referred to as the male hormone, while estrogen is known as the female hormone. However, men and women both produce these hormones, just in different amounts. A delicate balance between testosterone and estrogen is essential for proper functioning. When testosterone levels increase, such as during TRT, some of it is naturally converted into estrogen through a process called aromatization. This conversion is normal and necessary, but in some cases, it can result in excess estrogen levels.
High estrogen levels in men can trigger the development of gynecomastia. Estrogen stimulates the growth of breast tissue, and when the balance between testosterone and estrogen is disrupted, this tissue can grow abnormally. For men undergoing TRT, the risk of gynecomastia is influenced by how much testosterone is converted into estrogen and how well their bodies handle this hormonal shift.
Gynecomastia caused by TRT can present several challenges. Physically, men may notice swelling, tenderness, or a firm lump under the nipple area. These symptoms can range from mild to severe. Beyond the physical effects, gynecomastia often has a significant emotional and psychological impact. Many men feel embarrassed or self-conscious about their appearance, which can lead to anxiety, depression, or social withdrawal. This is why understanding and addressing gynecomastia is crucial for anyone considering or undergoing TRT.
The purpose of this article is to provide a detailed exploration of how TRT can lead to gynecomastia and what steps can be taken to manage or prevent it. Throughout the article, we will examine the mechanisms behind testosterone replacement therapy, explain how gynecomastia develops, and discuss the various treatment options available. We will also address ways to prevent gynecomastia, the role of lifestyle factors, and the importance of working closely with healthcare providers to achieve a safe and effective balance of hormones.
By shedding light on this topic, the goal is to help men make informed decisions about their health. Whether you are already on TRT, considering starting treatment, or simply curious about the risks and benefits, this article will provide the knowledge you need. Gynecomastia is a treatable condition, and with proper monitoring and care, many men can avoid or successfully manage its effects while benefiting from the improvements TRT offers.
In the following sections, we will explore these issues in depth, starting with a closer look at testosterone replacement therapy and gynecomastia itself. Understanding these concepts is the first step in empowering men to take control of their health and well-being.
What Is Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)?
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a medical treatment designed to address low testosterone levels in men. Testosterone is a critical hormone that plays a role in many aspects of male health, including muscle growth, bone strength, mood, energy levels, and sexual function. When testosterone levels drop below normal, it can lead to various symptoms and health issues. TRT is used to restore these levels to a healthy range, improving quality of life and addressing the symptoms of low testosterone.
Understanding Testosterone and Its Role
Testosterone is a hormone primarily produced in the testes in men, with small amounts made by the adrenal glands. It plays a vital role in several key bodily functions, such as:
- Developing male characteristics: Testosterone is responsible for the development of male traits, such as facial hair, a deep voice, and increased muscle mass.
- Maintaining sexual health: It supports libido (sex drive) and helps in sperm production.
- Regulating physical health: Testosterone aids in bone density, red blood cell production, and muscle strength.
- Boosting mental health: It can influence mood, energy, and cognitive function.
Low levels of testosterone, a condition called hypogonadism, can negatively impact these functions. Men with this condition often experience fatigue, reduced sex drive, mood changes, and muscle loss. TRT is a treatment designed to restore hormonal balance and address these issues.
Why Do Men Need Testosterone Replacement Therapy?
There are several reasons why testosterone levels may drop and TRT becomes necessary:
- Aging: Testosterone levels naturally decline as men age, typically starting in their 30s or 40s. This is often referred to as andropause or “male menopause.”
- Medical conditions: Certain illnesses or conditions can reduce testosterone levels, such as testicular injury, pituitary disorders, or genetic conditions like Klinefelter syndrome.
- Lifestyle factors: Stress, obesity, poor diet, and lack of exercise can also contribute to low testosterone levels.
Doctors prescribe TRT to alleviate the symptoms of low testosterone, such as:
- Chronic fatigue
- Loss of muscle mass
- Decreased libido
- Mood swings or depression
- Difficulty concentrating or memory problems
How Is TRT Administered?
TRT can be administered in different ways depending on the patient's preferences, medical history, and doctor's recommendations. The most common methods include:
- Injections:
Testosterone injections are administered directly into the muscle, typically every 1 to 2 weeks. They deliver a high dose of testosterone that gradually decreases until the next injection.- Pros: Effective and fast-acting.
- Cons: Can cause hormonal fluctuations between doses, leading to highs and lows in energy and mood.
- Gels or Creams:
Topical testosterone products are applied to the skin, usually on the arms or abdomen. They allow for steady absorption into the bloodstream.- Pros: Easy to apply and maintain stable testosterone levels.
- Cons: Risk of transferring the hormone to others through skin contact.
- Patches:
These are adhesive patches placed on the skin that release testosterone slowly over 24 hours.- Pros: Convenient and steady absorption.
- Cons: Can cause skin irritation for some users.
- Pellets:
Tiny pellets containing testosterone are implanted under the skin, usually in the hip or buttock. These pellets slowly release testosterone over several months.- Pros: Long-lasting and low-maintenance.
- Cons: Requires a minor surgical procedure to insert and remove.
- Oral or Buccal Tablets:
These are tablets or patches placed on the gums that release testosterone directly into the bloodstream.- Pros: Avoids the liver, where oral testosterone pills can be broken down.
- Cons: Requires consistent placement and replacement.
Each method has advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on the patient's lifestyle and preferences. A doctor will recommend the best option based on individual needs.
Benefits of TRT
For men suffering from low testosterone, TRT offers several potential benefits:
- Improved energy levels: Restoring testosterone can help combat fatigue and increase overall vitality.
- Better mood: Many men experience reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety with balanced testosterone levels.
- Enhanced physical performance: TRT can help rebuild muscle mass and improve endurance.
- Increased libido and sexual function: Restoring testosterone often improves sex drive and performance.
- Bone health: It strengthens bones, reducing the risk of fractures, especially in older men.
Risks and Considerations
While TRT can be life-changing for men with low testosterone, it is not without risks. Common side effects include acne, fluid retention, and increased red blood cell count. Long-term risks may include an increased likelihood of heart disease, prostate problems, and, in some cases, gynecomastia (enlargement of male breast tissue).
Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is essential to ensure that testosterone levels remain within a safe range and to minimize potential complications.
TRT is a powerful tool for improving the quality of life in men with low testosterone. Understanding its methods, benefits, and risks can help men make informed decisions about their health and treatment options.
What Is Gynecomastia?
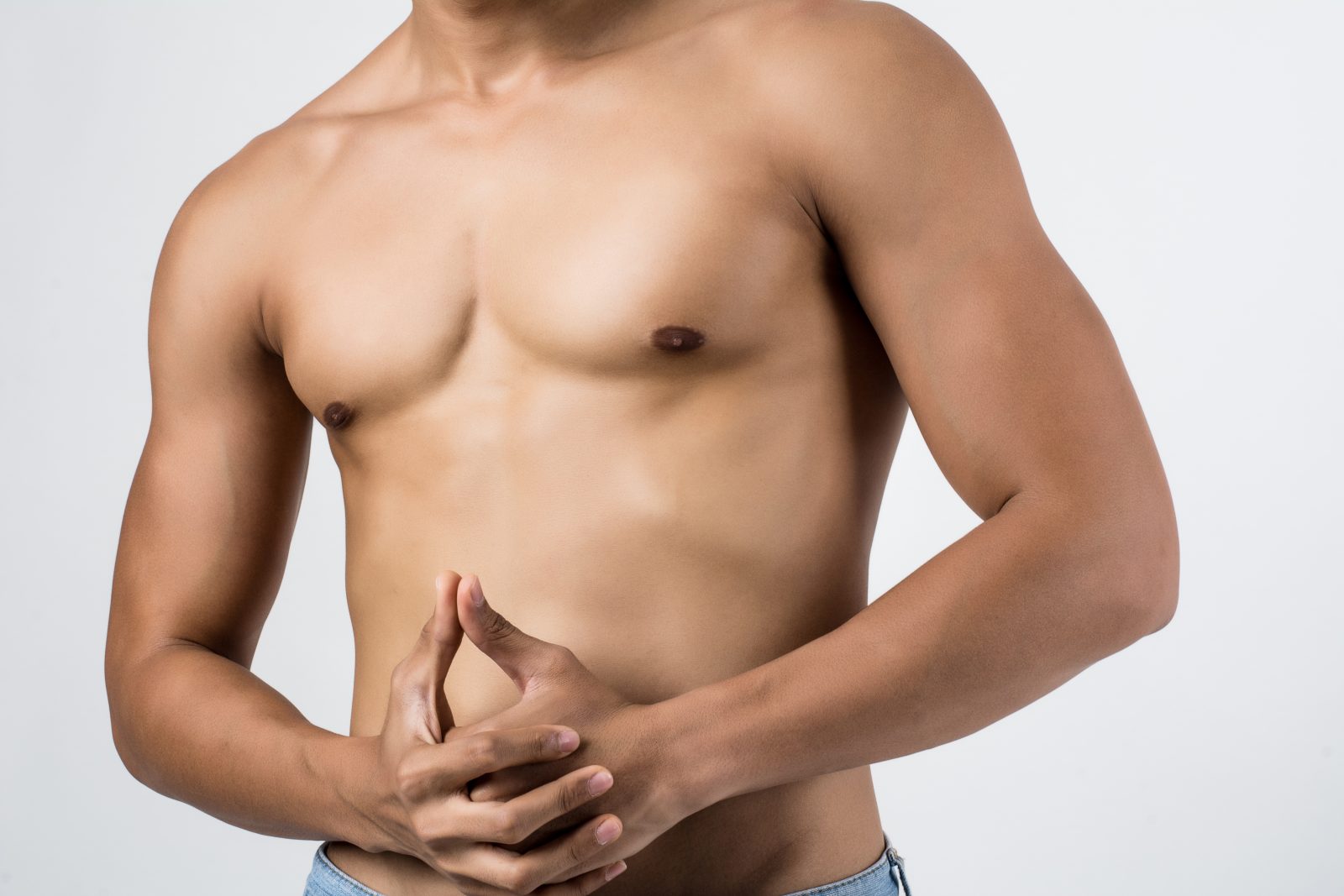
Gynecomastia is a medical condition where men develop enlarged breast tissue. It occurs when the breast gland tissue grows abnormally due to hormonal imbalances. This condition can affect one or both breasts, and it may develop unevenly. Gynecomastia is not rare; it is estimated that between 30% and 70% of men will experience it at some point in their lives. This condition can cause physical discomfort and emotional distress, making it an important issue to understand.
What Causes Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is primarily caused by an imbalance between two key hormones in the body: testosterone and estrogen. Testosterone is the male sex hormone that promotes masculine traits like muscle growth, a deeper voice, and body hair. Estrogen, while commonly thought of as a female hormone, is also present in men. It plays a smaller role in male physiology but becomes problematic when its levels are too high relative to testosterone.
When the balance shifts toward higher estrogen levels or lower testosterone levels, breast tissue in men can start to grow. This hormonal imbalance can occur naturally or as a side effect of certain conditions, medications, or therapies like testosterone replacement therapy (TRT).
Who Is Affected by Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia can affect males of all ages, but certain life stages are more prone to hormonal changes that might trigger the condition:
- Newborns: Many newborn boys have temporary gynecomastia due to the transfer of estrogen from the mother during pregnancy. This type of gynecomastia usually resolves on its own within a few weeks after birth.
- Adolescents: During puberty, hormonal fluctuations are common. Teenage boys may experience temporary gynecomastia as their bodies adjust to changing testosterone and estrogen levels. In most cases, this resolves within six months to two years.
- Adults: Gynecomastia is also common in older men, especially after the age of 50. As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline, and body fat tends to increase. Higher body fat can lead to more estrogen production, increasing the risk of gynecomastia.
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
The most noticeable symptom of gynecomastia is the enlargement of the breast area. However, this enlargement is not due to fat alone. It involves the growth of glandular tissue, which feels firmer or rubbery compared to soft fatty tissue.
Other symptoms may include:
- Breast tenderness or pain: Some men may feel soreness in the breast area.
- Swelling: This can occur in one or both breasts, making them appear uneven.
- Nipple sensitivity: In some cases, the nipples may become more sensitive to touch or pressure.
While gynecomastia is generally harmless, it is important to rule out other causes of breast swelling or lumps, such as tumors or infections.
Differences Between Gynecomastia and Pseudogynecomastia
It is important to differentiate gynecomastia from a similar-looking condition called pseudogynecomastia. Pseudogynecomastia is caused by an accumulation of fat in the chest area rather than glandular breast tissue growth. This condition is often seen in overweight or obese men. Unlike gynecomastia, pseudogynecomastia does not involve hormonal imbalances and can often be addressed with weight loss and exercise.
In some cases, the two conditions can occur together. A medical evaluation, which may include a physical exam or imaging tests like ultrasound, can help distinguish between the two.
How Gynecomastia Affects Men
Gynecomastia can have both physical and emotional impacts. Physically, the enlargement and tenderness of breast tissue can be uncomfortable, particularly during activities like exercise. In severe cases, it can interfere with daily life and reduce quality of life.
Emotionally, gynecomastia can affect self-esteem and body image. Many men feel embarrassed or self-conscious about the condition, especially in situations where their chest is exposed, such as swimming or gym activities. The psychological effects of gynecomastia should not be overlooked, as they can lead to anxiety, depression, and social withdrawal.
The Importance of Seeking Medical Advice
If you suspect you have gynecomastia, it is important to consult a healthcare provider. A thorough medical evaluation can help determine whether the condition is true gynecomastia or pseudogynecomastia. The doctor will also look for underlying causes, such as medication use, hormonal disorders, or other health conditions.
By identifying the cause of gynecomastia, your doctor can recommend an appropriate treatment plan. Early diagnosis can help prevent complications and alleviate discomfort.
Gynecomastia is a condition that causes the enlargement of breast tissue in men, often due to hormonal imbalances between testosterone and estrogen. It can occur at different stages of life and has both physical and emotional effects. Differentiating between gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia is key to choosing the right treatment. Understanding this condition can help men take the necessary steps to address it effectively.
How Does TRT Contribute to Gynecomastia?
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) can be life-changing for men with low testosterone levels. It helps improve energy, mood, muscle growth, and overall quality of life. However, a side effect that some men may experience is gynecomastia, or the enlargement of breast tissue. This condition can be caused by hormonal changes in the body that are influenced by TRT. To understand this, it’s important to explore the role of estrogen in male physiology, the process of aromatization, and how these changes can lead to gynecomastia.
The Role of Estrogen in Male Physiology
Many people think of estrogen as a "female hormone," but men also produce it in small amounts. In males, estrogen plays several important roles, such as:
- Regulating bone density: Estrogen helps maintain strong bones. Low estrogen levels can lead to osteoporosis, even in men.
- Supporting brain function: Estrogen is involved in mood regulation and cognitive processes.
- Maintaining cardiovascular health: Estrogen contributes to healthy blood flow and heart function.
Estrogen is essential for men’s health, but its levels must remain balanced. Too much estrogen in the male body can disrupt this balance, leading to physical changes such as gynecomastia.
What Is Aromatization?
Aromatization is a natural process in which the body converts testosterone into estrogen. This conversion is carried out by an enzyme called aromatase. While some testosterone is always converted to estrogen, certain factors can increase the rate of aromatization, such as:
- High levels of testosterone in the bloodstream: When a man undergoes TRT, the testosterone levels in his body rise significantly. This can give the aromatase enzyme more raw material (testosterone) to convert into estrogen.
- Body fat percentage: Aromatase is more active in fat tissue. Men with higher body fat are more likely to convert testosterone into estrogen.
- Genetics: Some men naturally produce more aromatase than others, which can increase their risk of developing gynecomastia during TRT.
When estrogen levels rise too high, the hormone can bind to breast tissue receptors, causing glandular growth and swelling.
How Elevated Estrogen Levels Lead to Gynecomastia
When testosterone is converted into estrogen at an increased rate, the resulting hormonal imbalance can cause noticeable changes in the male body. Here’s how elevated estrogen contributes to gynecomastia:
- Stimulation of Breast Tissue Growth:
Estrogen promotes the growth of glandular breast tissue. In men on TRT, elevated estrogen levels can overstimulate this tissue, leading to visible swelling. - Inhibition of Testosterone’s Effects:
High estrogen levels can counteract the benefits of testosterone. This imbalance can disrupt the hormonal signals that maintain male physical traits, allowing breast tissue to grow. - Increased Water Retention:
Estrogen is linked to water retention in the body. This can make the chest area appear puffier, adding to the visual signs of gynecomastia. - Hormonal Feedback Loops:
The body tries to maintain balance through feedback mechanisms. If estrogen levels spike too high, the body might reduce its natural testosterone production further, worsening the imbalance.
The Importance of Hormone Balance During TRT
The key to avoiding gynecomastia while on TRT is maintaining a proper balance between testosterone and estrogen. Doctors carefully monitor hormone levels during TRT to prevent complications. This typically involves regular blood tests to measure:
- Total testosterone levels
- Free testosterone (the active form of testosterone in the blood)
- Estradiol (a form of estrogen) levels
By closely tracking these values, healthcare providers can adjust TRT dosages to ensure that testosterone levels are optimal without triggering excessive aromatization.
Why Some Men Are More Prone to Gynecomastia
Not all men on TRT develop gynecomastia. Some factors that can increase the likelihood include:
- Higher body fat: As mentioned earlier, more fat tissue means more aromatase activity.
- Pre-existing hormonal imbalances: Men who naturally produce higher levels of estrogen or have conditions like Klinefelter syndrome are at greater risk.
- Improper TRT dosing: Overdosing on testosterone can flood the system and accelerate aromatization.
While TRT can significantly improve a man’s quality of life, it has the potential to cause hormonal imbalances that lead to gynecomastia. Understanding the role of estrogen, the aromatization process, and the importance of hormone balance is crucial. Regular monitoring and individualized treatment plans can minimize the risk and ensure safe, effective therapy. By addressing these factors, men on TRT can enjoy its benefits while reducing the likelihood of developing gynecomastia.
Signs and Symptoms of Gynecomastia in Men on TRT
Gynecomastia can be a concerning side effect for men undergoing testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). It occurs when there is an imbalance in hormones, particularly testosterone and estrogen, leading to the development of excess breast tissue in males. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of gynecomastia early is essential for timely intervention. Below, we explore the physical, emotional, and psychological impacts of this condition and discuss when it’s important to seek medical advice.
Physical Symptoms of Gynecomastia
The physical symptoms of gynecomastia are often the most noticeable and can range from mild to severe. These symptoms usually affect one or both breasts and include the following:
- Swelling of Breast Tissue
The most common sign of gynecomastia is an increase in breast tissue size. This swelling is not fat but glandular tissue growth, which is firmer to the touch than typical body fat. It often starts as a small, rubbery lump under the nipple and can grow larger over time. - Tenderness or Pain in the Breasts
Many men with gynecomastia report tenderness or soreness in the affected area. The sensitivity may worsen with pressure or touch. Pain levels vary, but even mild discomfort can interfere with daily activities and sleep. - Asymmetry in Breast Growth
Gynecomastia may affect one breast more than the other, leading to noticeable asymmetry. This uneven development can sometimes be mistaken for other conditions, such as a cyst or tumor. - Skin Changes Around the Nipple Area
In some cases, gynecomastia may cause stretching of the skin around the nipples due to tissue growth. The nipples might also appear more prominent or slightly puffy.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
The physical changes caused by gynecomastia can have significant emotional and psychological effects. Men may feel self-conscious or embarrassed about their appearance, particularly if the condition becomes visible through clothing. Here are some common emotional responses:
- Low Self-Esteem and Body Image Issues
Men with gynecomastia often report a loss of confidence in their physical appearance. This is especially true in situations where they might need to remove their shirts, such as at the beach or while playing sports. - Social Withdrawal
Feeling self-conscious about breast enlargement can lead to avoidance of social situations or activities where others might notice the condition. This withdrawal can impact relationships and overall quality of life. - Anxiety and Stress
Some men experience anxiety about their health, worrying that breast swelling could signal a more serious condition like breast cancer. This stress can worsen if they delay seeking medical advice. - Depression and Mood Changes
Persistent feelings of embarrassment, coupled with changes in self-image, can contribute to depression. It’s important to recognize when emotional struggles go beyond normal and require professional support.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Gynecomastia may resolve on its own in some cases, but it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider if you notice any of the following:
- Rapid Onset of Symptoms
If breast enlargement occurs suddenly or progresses quickly, it could indicate a more serious underlying issue, such as a hormonal imbalance or medication reaction. - Severe Pain or Discomfort
While mild tenderness is common, severe or persistent pain should be evaluated. This might indicate complications or the need for more targeted treatment. - Unusual Discharge or Changes in the Nipple
Nipple discharge, changes in color, or other unusual symptoms could be a sign of a different condition and warrant immediate medical attention. - Persistent Swelling That Doesn’t Improve
If gynecomastia persists for more than six months, it’s important to seek evaluation. Chronic gynecomastia may require medication or surgical intervention to resolve.
How to Address Concerns With Your Doctor
When consulting your healthcare provider, be prepared to share details about your symptoms, including:
- When the swelling or tenderness started
- Whether symptoms have worsened or improved over time
- Any medications or supplements you’re taking, including TRT dosage
- Any history of hormonal issues or similar conditions
A doctor may conduct a physical examination, recommend blood tests to check hormone levels, or suggest imaging studies like an ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis.
Gynecomastia in men undergoing TRT can cause both physical and emotional distress. Recognizing the signs—such as breast swelling, tenderness, and changes in appearance—is the first step in managing the condition. Seeking medical advice early is important to rule out other causes, receive appropriate treatment, and address any psychological concerns. By understanding these symptoms and their potential impact, men can take proactive steps to manage their health and well-being.
Diagnosing Gynecomastia in Men on TRT
Diagnosing gynecomastia in men undergoing testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is an essential step in addressing this condition. Gynecomastia is the enlargement of breast tissue in men due to hormonal imbalances. Early and accurate diagnosis ensures proper treatment and prevents unnecessary complications. This section explains the process of diagnosing gynecomastia in detail, including physical exams, hormonal testing, and imaging studies.
Physical Examination and History Taking
The first step in diagnosing gynecomastia is a thorough physical examination and a detailed medical history. During the examination, the doctor will check the breast tissue to determine if the enlargement is caused by fat (pseudogynecomastia) or true glandular growth (gynecomastia). Key aspects of this step include:
- Physical Inspection
- The doctor will examine the size, shape, and firmness of the breast tissue.
- True gynecomastia often presents as a firm or rubbery disc of tissue beneath the nipple.
- Pseudogynecomastia, caused by excess fat, is softer and spread more diffusely.
- Medical History
- The doctor will ask about the patient’s symptoms, such as tenderness, pain, or nipple discharge.
- Questions about lifestyle, medication use, and TRT dosage are common.
- A history of hormone-related conditions, such as hypogonadism, or past use of substances like anabolic steroids or alcohol, may be discussed.
- Family History
- Some cases of gynecomastia may have a genetic component. A family history of breast conditions or hormonal imbalances can provide clues.
This step helps the doctor determine if further testing is necessary.
Hormonal Testing
Hormonal imbalances are the leading cause of gynecomastia, especially in men on TRT. Hormonal testing is a critical diagnostic tool to identify these imbalances. Common tests include:
- Testosterone Levels
- TRT aims to normalize testosterone levels, but an excessive dose can lead to elevated levels.
- Elevated testosterone may convert to estrogen through a process called aromatization, triggering gynecomastia.
- Estrogen Levels
- Estrogen is present in small amounts in men but can rise during TRT, especially if aromatization is not managed.
- High estrogen levels are a significant contributor to breast tissue growth in men.
- Prolactin Testing
- Elevated prolactin levels, though less common, can cause gynecomastia. Prolactin is a hormone associated with breast tissue development.
- Other Hormones
- Tests may include luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and thyroid hormones to rule out other causes of gynecomastia.
- Cortisol levels might also be tested to ensure that conditions like Cushing’s syndrome are not contributing.
Hormonal testing provides a clear picture of the body’s internal balance, helping the doctor identify the root cause of gynecomastia.
Imaging Studies
If physical exams and hormone tests are inconclusive, imaging studies may be used to confirm the diagnosis. Imaging helps rule out other conditions, such as breast cancer, which can mimic gynecomastia. Common imaging methods include:
- Ultrasound
- Ultrasound is the most frequently used imaging tool to evaluate breast tissue.
- It can distinguish between fatty tissue and glandular tissue, helping confirm gynecomastia.
- This test is non-invasive and painless, making it a preferred choice.
- Mammogram
- While mammograms are typically associated with women, they can also be used in men to detect abnormalities in breast tissue.
- A mammogram is recommended if there are suspicious features, such as a hard lump or nipple discharge.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
- MRI is less commonly used but can provide detailed images of the breast tissue when other methods are insufficient.
- It is particularly useful in complex cases or when cancer is suspected.
- CT Scans and Other Imaging
- These may be used if the doctor suspects a broader hormonal issue or tumors affecting hormone levels.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It is important to consult a healthcare provider if gynecomastia symptoms appear. These symptoms include swelling, tenderness, or changes in the breast area. Men on TRT should be vigilant about reporting any new or unusual symptoms. Seeking medical advice promptly allows for early intervention and better outcomes.
Diagnosing gynecomastia involves a combination of physical exams, hormonal testing, and imaging studies. This multi-step approach ensures that the underlying cause is identified and treated appropriately. By working closely with a healthcare provider, men on TRT can address gynecomastia effectively and continue their therapy with confidence.
Preventing Gynecomastia While on TRT
Preventing gynecomastia (enlarged male breast tissue) while undergoing testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is important for maintaining both physical and emotional well-being. Gynecomastia can develop as a side effect of TRT when hormone levels become imbalanced, especially if testosterone converts to estrogen at a higher rate than expected. The following steps can help minimize the risk of gynecomastia for those undergoing TRT.
- Monitor Estrogen Levels During Therapy
When you start TRT, your body may convert some of the testosterone into estrogen through a natural process called aromatization. High estrogen levels can lead to breast tissue growth. Regular monitoring of estrogen levels is essential to catch any imbalance early.
- Why Monitoring Matters: Estrogen plays an important role in male health, but too much can lead to unwanted side effects like gynecomastia. Blood tests measuring estradiol (a form of estrogen) can show whether levels are rising too much during TRT.
- How Often to Test: At the beginning of therapy, your doctor may check hormone levels every few weeks. Once your levels are stable, testing every few months might be enough.
- Role of Aromatase Inhibitors (AIs) in Prevention
Aromatase inhibitors are medications that block the conversion of testosterone into estrogen. They can help keep estrogen levels within a normal range and reduce the risk of gynecomastia.
- Common AIs Used:
Medications like anastrozole and letrozole are examples of AIs that may be prescribed during TRT. These drugs slow down the aromatase enzyme, reducing estrogen production. - Risks and Benefits:
While AIs can be effective, they should only be used under a doctor’s guidance. Too little estrogen can cause its own problems, such as joint pain, fatigue, and reduced bone density. Finding the right balance is key.
- Adjusting TRT Dosage and Frequency
The dose and timing of testosterone administration can influence how much testosterone is converted to estrogen.
- Starting Low and Going Slow:
Some men may start with a higher dose of testosterone, leading to a spike in estrogen levels. Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it allows the body to adjust without overwhelming the hormone balance. - Injection vs. Other Methods:
For men using injections, smaller, more frequent doses can help prevent sudden peaks in testosterone, which can lead to increased aromatization. For example, instead of one large injection every two weeks, splitting the dose into smaller injections once or twice a week can keep levels steadier. - Other Administration Methods:
Gels, patches, or pellets may also result in more stable testosterone levels compared to infrequent injections. Discussing the best method with your doctor can make a big difference.
- Importance of Individualized Treatment Plans
Not all men respond to TRT in the same way. Factors like body composition, genetics, age, and overall health can affect how your body processes testosterone.
- Personalized Testing:
A healthcare provider will consider your unique hormone levels before prescribing TRT. Ongoing adjustments to your treatment plan may be necessary to ensure you stay in balance. - Body Fat and Aromatization:
Men with higher body fat percentages are more likely to convert testosterone into estrogen, as fat cells contain more aromatase enzymes. Managing weight and reducing body fat through diet and exercise can support a balanced hormonal response to TRT.
- Staying in Close Contact with Your Doctor
Preventing gynecomastia while on TRT requires teamwork between you and your healthcare provider.
- Regular Follow-Ups:
Scheduling regular appointments allows your doctor to adjust your treatment if needed. If estrogen levels rise or you notice symptoms of gynecomastia, changes can be made quickly to prevent worsening. - Communication:
If you notice swelling, tenderness, or other changes in your chest, let your doctor know immediately. Early intervention is crucial to managing gynecomastia effectively.
- Avoiding Over-the-Counter Remedies Without Guidance
Some men may turn to over-the-counter supplements that claim to prevent gynecomastia or control estrogen levels. These products are often not tested for safety or effectiveness and may interfere with your TRT.
- Stick to Doctor-Approved Options:
Only use medications and supplements prescribed or recommended by a healthcare professional to ensure they are safe and effective for your specific needs.
Preventing gynecomastia while on TRT is about maintaining hormonal balance. By monitoring estrogen levels, using medications like AIs when needed, adjusting dosages, and working closely with your doctor, you can significantly reduce the risk of this side effect. Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as managing body fat, can also support balanced hormones and improve your overall TRT experience. Always follow a personalized treatment plan tailored to your body’s unique needs for the best results.
Treating Gynecomastia Induced by TRT
Gynecomastia caused by testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can be distressing, but it is treatable. Treatment options range from non-invasive approaches like medications to surgical procedures for more severe cases. Choosing the right treatment depends on the severity of the gynecomastia, how long it has been present, and the individual’s overall health. Let’s explore these options in detail.
Non-Surgical Options: Medications
In the early stages of gynecomastia, medications may be effective in reducing breast tissue growth. These treatments aim to target the hormonal imbalance that causes gynecomastia. Here are the primary options:
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs)
- Tamoxifen and Raloxifene are the most commonly used SERMs.
- These medications block the effects of estrogen on breast tissue, helping to reduce the size of the glandular tissue.
- They are particularly effective when used in the early stages of gynecomastia, within the first six months of development.
- How they work: SERMs bind to estrogen receptors in the breast tissue, preventing estrogen from stimulating growth.
Aromatase Inhibitors (AIs)
- Examples include Anastrozole and Letrozole.
- These medications work by reducing the amount of estrogen in the body.
- AIs block the enzyme aromatase, which converts testosterone into estrogen.
- When they are used: AIs are particularly useful when high estrogen levels are identified as a significant contributor to gynecomastia.
Considerations for Medications
- Medications are most effective for gynecomastia in its early stages.
- They are less likely to work on long-standing gynecomastia where fibrous tissue has developed.
- Always consult a healthcare provider before starting these treatments to discuss potential side effects and proper dosages.
Surgical Options: Permanent Solutions for Severe Cases
When gynecomastia persists or is severe, surgery may be the most effective treatment. Surgical interventions are designed to remove excess glandular tissue, fat, or both. The two main surgical procedures are:
Liposuction
- What it addresses: Liposuction targets excess fatty tissue in the chest.
- How it works: During the procedure, small incisions are made in the chest area, and a thin tube (cannula) is inserted to suction out the fat.
- Recovery time: Most patients can resume normal activities within a few weeks, though strenuous activities may need to be avoided longer.
- Benefits: This procedure is less invasive and results in minimal scarring.
Glandular Excision
- What it addresses: Excision surgery is necessary to remove firm glandular tissue that cannot be treated with liposuction alone.
- How it works: The surgeon makes an incision around the edge of the areola (the dark area around the nipple) to remove the glandular tissue directly.
- When it’s used: This method is ideal for patients with significant glandular enlargement or long-standing gynecomastia.
- Recovery time: Full recovery may take several weeks to months, depending on the extent of the surgery.
Combination of Liposuction and Excision
- In many cases, surgeons use both techniques to achieve the best cosmetic results.
- Fat is removed through liposuction, while glandular tissue is excised.
When Is Surgery Recommended?
- Surgery is recommended when:
- Gynecomastia has persisted for over a year without improvement.
- The condition causes significant pain, tenderness, or psychological distress.
- Medications have been ineffective in reducing the breast tissue.
- There is significant glandular tissue that will not respond to non-surgical treatments.
The Role of Follow-Up Care
Post-treatment care is crucial to ensure a smooth recovery and prevent recurrence. Here’s what patients should keep in mind:
- Regular follow-ups: Monitor hormone levels and overall health with a doctor.
- Compression garments: These are often recommended after surgery to reduce swelling and support the chest during healing.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Maintain a healthy weight and avoid substances like alcohol or drugs that can increase estrogen levels.
- Monitoring TRT: Work closely with your healthcare provider to adjust testosterone doses and prevent hormonal imbalances in the future.
Treating gynecomastia caused by TRT requires a tailored approach. Early intervention with medications can be effective, but persistent or severe cases may require surgery. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action based on your specific situation. With proper treatment and follow-up care, most individuals can achieve relief from symptoms and restore their confidence.
Common Misconceptions About TRT and Gynecomastia
When it comes to testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) and gynecomastia, there are many misconceptions. These misunderstandings can create confusion and sometimes even prevent people from seeking the right treatment. Below, we will address and explain some of the most common myths to give you a clearer picture.
Myth 1: TRT Is the Sole Cause of Gynecomastia
Many people believe that testosterone replacement therapy directly causes gynecomastia. While there is a connection, the reality is more complex. Gynecomastia happens when there is an imbalance between male and female hormones in the body. Specifically, high levels of estrogen (a hormone more dominant in women) in men can lead to the development of breast tissue.
TRT itself doesn’t inherently cause this imbalance. Instead, it’s the body’s response to the extra testosterone. When testosterone is introduced into the body, some of it converts into estrogen through a process called aromatization. For some men, this increased estrogen can tip the hormonal balance and lead to gynecomastia. However, not everyone experiences this side effect. The risk depends on factors like genetics, dosage, and individual sensitivity to hormonal changes.
It’s important to understand that TRT is just one piece of the puzzle. Gynecomastia can also result from other factors such as certain medications, health conditions, or natural hormone fluctuations.
Myth 2: All Men on TRT Will Develop Gynecomastia
This is another widespread misunderstanding. Not all men who undergo TRT will develop gynecomastia. Many factors influence whether this condition occurs, including:
- Dosage: Higher doses of testosterone can increase the likelihood of excess estrogen being produced.
- Body Composition: Men with higher levels of body fat may be more prone to gynecomastia because fat cells can convert testosterone into estrogen.
- Genetics: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to hormonal imbalances, which can make them more likely to develop gynecomastia.
With proper monitoring and individualized care, most men on TRT can avoid gynecomastia altogether. Regular blood tests to check hormone levels, including testosterone and estrogen, are critical in preventing this issue.
Myth 3: Gynecomastia Is the Same as Pseudogynecomastia
Some men confuse gynecomastia with pseudogynecomastia, but the two are not the same. Gynecomastia is caused by an overgrowth of glandular breast tissue due to hormonal imbalances. Pseudogynecomastia, on the other hand, is the accumulation of fat in the chest area, which can look similar to gynecomastia but is unrelated to hormones.
This distinction is important because the treatments are different. Gynecomastia might require medications or surgery to remove glandular tissue, while pseudogynecomastia can often be addressed with weight loss, exercise, and a healthy diet. A doctor can help identify the condition through a physical exam and imaging, such as an ultrasound.
Myth 4: Aromatase Inhibitors Are Dangerous
Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) are medications that block the enzyme responsible for converting testosterone into estrogen. Many men fear that using AIs is harmful or will cause severe side effects. However, when prescribed and used correctly, AIs can effectively manage estrogen levels and reduce the risk of gynecomastia.
Like any medication, AIs can cause side effects, such as joint pain or changes in mood, but these are usually mild and manageable. It is important to note that AIs are not for everyone. They should only be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider who can adjust the dosage based on your needs and monitor for side effects.
Myth 5: Gynecomastia Will Always Go Away on Its Own
Some men believe that gynecomastia caused by TRT will resolve without treatment. While it’s true that mild cases may improve if hormone levels are balanced, this isn’t always the case. Long-term gynecomastia can cause permanent changes in the breast tissue, making it difficult to reverse without surgery. If you notice symptoms of gynecomastia, it’s essential to consult a doctor early to explore your options.
Myth 6: TRT Is Unsafe Because of the Risk of Gynecomastia
The final misconception is that TRT is dangerous because of its association with gynecomastia. While the risk exists, it is usually manageable with proper medical care. TRT has been proven to be a safe and effective treatment for men with low testosterone when monitored correctly. The benefits, such as improved energy, mood, and muscle mass, often outweigh the risks for most men.
By understanding how TRT works and partnering with a knowledgeable healthcare provider, you can reduce the likelihood of side effects, including gynecomastia.
Misconceptions about TRT and gynecomastia can lead to unnecessary fear and confusion. Knowing the facts is the first step toward making informed decisions about your health. If you are on TRT or considering it, work closely with your doctor to monitor your hormone levels and address any concerns. With the right approach, you can minimize risks and enjoy the benefits of therapy.
Addressing the Psychological Impact of Gynecomastia in Men
Gynecomastia, or the enlargement of breast tissue in men, is more than just a physical condition. It can have a profound impact on a man’s mental and emotional well-being. For men undergoing testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), developing gynecomastia can feel particularly distressing because TRT is often sought to improve overall health and confidence. In this section, we will explore the psychological effects of gynecomastia, strategies for coping, and the importance of support systems.
The Emotional and Mental Health Challenges of Gynecomastia
For many men, physical appearance plays an important role in self-esteem and confidence. The development of gynecomastia can create feelings of embarrassment or shame. Men may feel that their bodies appear less traditionally masculine, which can affect how they see themselves.
- Self-Consciousness and Social Anxiety: Men with gynecomastia may feel uncomfortable wearing tight or light-colored shirts, participating in sports, or going shirtless in public. This can lead to social withdrawal and avoidance of situations like going to the gym or the beach.
- Emotional Distress: The condition can cause frustration and even anger, particularly for those who have invested time and effort into improving their health through TRT. Feeling betrayed by their own body is common.
- Depression and Anxiety: Some men may experience deeper psychological challenges, such as depression or generalized anxiety, especially if the gynecomastia remains untreated or worsens over time.
Seeking Professional Mental Health Support
For men struggling with the psychological impact of gynecomastia, seeking help from a mental health professional can be a crucial first step. Therapists or counselors who specialize in body image issues can provide guidance and coping tools.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This type of therapy can help men challenge negative thoughts about their appearance and develop healthier perspectives about their body.
- Stress Management: Learning to manage stress through techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or breathing exercises can reduce the emotional toll of the condition.
- Medication: In some cases, a doctor or psychiatrist may recommend medications to manage symptoms of depression or anxiety.
Building Confidence Through Open Communication
Talking about gynecomastia can feel awkward, but open communication is an important part of overcoming its psychological effects. Many men feel relieved when they discuss their concerns with someone they trust, whether that is a friend, partner, or healthcare provider.
- Speaking with a Healthcare Provider: A doctor who understands gynecomastia can provide medical insights and treatment options. This can help alleviate fears or misconceptions about the condition.
- Talking to Loved Ones: Sharing feelings with close family members or partners can create a sense of support and understanding. Often, loved ones can provide reassurance that physical appearance does not define a person’s worth.
Finding Peer Support
Joining a support group or online community can help men feel less isolated. These groups allow men to connect with others who are experiencing similar challenges, exchange tips for coping, and discuss potential treatment options.
- In-Person Support Groups: Some hospitals or clinics offer support groups for individuals dealing with gynecomastia or other body image concerns.
- Online Communities: Platforms such as Reddit or health forums have groups dedicated to gynecomastia, where men can share experiences and advice anonymously.
Rebuilding Confidence Through Self-Care
Taking care of one’s overall health can play a big role in managing the psychological impact of gynecomastia. When men focus on what they can control, it can improve their outlook and self-esteem.
- Exercise and Fitness: While exercise alone cannot cure gynecomastia, it can help maintain a healthy weight and improve overall body image. Strength training, in particular, can enhance muscle tone and create a more positive perception of one’s physique.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet not only supports physical health but can also improve mood and energy levels.
- Grooming and Appearance: Some men find that paying attention to other aspects of their appearance, such as personal grooming or updating their wardrobe, can boost confidence.
The Role of Self-Compassion
Finally, practicing self-compassion is key. Many men blame themselves for developing gynecomastia, but it is important to remember that the condition is not a reflection of personal failure. Being kind to oneself and focusing on what can be changed is a powerful way to regain confidence and peace of mind.
- Avoid Negative Self-Talk: Replace thoughts like “I look terrible” with more neutral statements like “I’m working on improving my health.”
- Celebrate Small Wins: Recognize efforts to address gynecomastia, whether through medical consultation or lifestyle changes.
Gynecomastia caused by TRT can take a toll on a man’s mental health, but understanding the emotional effects and seeking help can make a big difference. Whether it’s through therapy, support groups, or self-care, addressing the psychological impact is as important as treating the physical condition. With the right strategies, men can regain confidence and move forward with a positive outlook.
The Role of Lifestyle in Managing and Preventing Gynecomastia on TRT
Lifestyle choices play a significant role in managing and preventing gynecomastia (gyno) for individuals on testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). Making the right adjustments in your daily habits can help maintain a hormonal balance, reduce risks, and promote overall health. Below, we will explore key lifestyle factors, including diet, exercise, avoiding alcohol and certain medications, and managing body weight and fat levels.
Balanced Diet and Hormonal Health
A healthy and balanced diet is crucial for maintaining hormonal stability and preventing gynecomastia. Certain foods can influence testosterone and estrogen levels in the body, which are directly linked to the development of gyno.
- Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods
Include foods rich in vitamins and minerals, like leafy greens, lean proteins, whole grains, nuts, and seeds. These provide the nutrients your body needs to regulate hormones efficiently. - Reduce Processed Foods
Avoid foods high in refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives. These can contribute to weight gain and potentially disrupt your hormone levels by increasing estrogen production. - Include Foods That Support Hormone Balance
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts contain compounds that can help reduce estrogen levels.
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish (like salmon) support testosterone production.
- Fiber-Rich Foods: High-fiber foods improve digestion and can help eliminate excess estrogen through the gut.
- Avoid Estrogenic Foods
Certain foods, such as soy products, contain phytoestrogens, which mimic estrogen in the body. While small amounts are unlikely to cause problems, overconsumption may increase estrogen levels and risk of gyno.
Exercise to Maintain Hormonal Balance
Regular physical activity is another essential component of managing gynecomastia while on TRT. Exercise not only helps regulate hormone levels but also aids in maintaining a healthy weight, which reduces the likelihood of estrogen dominance.
- Strength Training
Weightlifting or resistance training increases testosterone levels naturally. Focus on compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses that engage large muscle groups and promote hormonal growth. - Cardiovascular Exercise
Cardio activities such as running, cycling, or swimming help burn calories and reduce body fat. Lower body fat levels can decrease the amount of testosterone that is converted to estrogen. - High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
HIIT workouts combine short bursts of intense activity with brief rest periods. This type of exercise has been shown to improve testosterone levels and enhance fat-burning capacity. - Consistency Matters
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise each week. A mix of strength and cardio exercises will yield the best results.
Avoid Alcohol and Estrogen-Boosting Substances
Alcohol and certain medications can increase estrogen levels, making gynecomastia more likely.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol intake can impair liver function, which is responsible for breaking down estrogen. This can lead to an increase in circulating estrogen levels in the body. - Beware of Certain Medications
Some medications, such as anabolic steroids, anti-androgens, and certain heart or ulcer drugs, can raise estrogen or suppress testosterone. Always consult your doctor about potential side effects of any medication you are taking. - Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water supports liver function and the body’s ability to maintain hormonal balance.
Manage Weight and Reduce Body Fat
High body fat levels are associated with increased estrogen production. Fat tissue contains an enzyme called aromatase, which converts testosterone into estrogen. Managing weight and reducing excess fat can help mitigate this risk.
- Maintain a Healthy Calorie Intake
Overeating, even healthy foods, can lead to weight gain. Work with a nutritionist or use online tools to calculate your caloric needs based on your activity level and goals. - Focus on Fat Loss, Not Just Weight Loss
Use strategies like exercise and proper nutrition to target fat loss while preserving lean muscle mass. Muscle tissue supports higher testosterone levels and helps keep estrogen in check. - Monitor Progress
Regularly check your weight and body composition to ensure that you are losing fat and building or maintaining muscle.
A Holistic Approach to Lifestyle Management
Addressing lifestyle factors involves more than just diet and exercise. It’s about making sustainable changes that support your body’s overall health. Here are a few additional tips:
- Sleep Well: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Sleep is crucial for testosterone production and stress reduction.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can lead to increased levels of cortisol, a hormone that may interfere with testosterone production. Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga.
- Stay Consistent: Small, consistent changes add up over time. Building good habits is key to maintaining hormonal balance and reducing the risk of gynecomastia.
By making these lifestyle adjustments, you can reduce the risk of gynecomastia while on TRT and improve your overall health. Remember, these strategies complement medical interventions, so always consult your healthcare provider for a personalized approach.
Conclusion: Achieving Balance in TRT and Managing Gynecomastia
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can be life-changing for men with low testosterone levels. It helps improve energy, muscle strength, mood, and overall quality of life. However, like any medical treatment, TRT comes with potential side effects. One of these side effects is gynecomastia, a condition where the male breast tissue grows larger. This happens because of hormonal imbalances, particularly when testosterone is converted into estrogen, a process called aromatization. Understanding this connection is crucial for preventing and managing gynecomastia effectively while staying on TRT.
The key to successfully navigating TRT while avoiding or addressing gynecomastia is balance. Hormones work together like a finely tuned system, and even small changes can lead to noticeable effects. During TRT, testosterone levels rise, which can cause the body to produce more estrogen. If estrogen levels get too high, it can stimulate breast tissue growth, leading to gynecomastia. Therefore, monitoring and maintaining proper hormone levels is one of the most important steps in managing this condition.
Preventing gynecomastia often starts with regular testing. When starting TRT, doctors typically measure baseline hormone levels, including testosterone and estrogen. These tests should be repeated regularly during treatment to catch any changes early. If estrogen levels start to climb, adjustments can be made before gynecomastia develops. For example, lowering the TRT dose or using an aromatase inhibitor (AI) can help reduce estrogen production. This proactive approach can prevent more serious issues down the road.
If gynecomastia does occur, there are options for treatment. In some cases, simply adjusting the TRT dose or adding medication to block estrogen's effects can help the breast tissue shrink. Medications like tamoxifen or raloxifene, called selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), are sometimes used to treat gynecomastia. These drugs work by blocking estrogen's action in the breast tissue, which can stop further growth and even reduce the size of existing tissue. However, these medications should only be used under the guidance of a doctor, as they can have their own side effects.
In more severe cases or when gynecomastia doesn’t go away with medication, surgery may be an option. Surgical treatments, like liposuction or glandular excision, can remove the excess breast tissue and restore a more masculine chest appearance. Liposuction is usually used for removing fatty tissue, while glandular excision is used to remove the firmer, glandular tissue common in gynecomastia. Sometimes, both techniques are combined for the best results. Recovery from surgery can take a few weeks, and the results are usually permanent. However, surgery is typically considered a last resort after other treatments have been tried.
Living with gynecomastia can be emotionally challenging. Men who experience this condition often feel self-conscious or embarrassed about their appearance. This can lead to anxiety, depression, or even withdrawal from social activities. Addressing these feelings is just as important as treating the physical symptoms. Talking to a counselor or joining a support group can help men cope with the emotional impact of gynecomastia. It’s important to remember that gynecomastia is a medical condition, not a personal failure, and effective treatments are available.
Lifestyle choices can also play a significant role in managing and preventing gynecomastia. Maintaining a healthy weight is particularly important since excess body fat can increase estrogen production. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can support overall hormone health. Regular exercise, especially strength training, helps improve testosterone levels and reduce body fat, further lowering the risk of gynecomastia. Avoiding substances that can increase estrogen, like excessive alcohol, certain medications, and recreational drugs, is another practical step men can take.
The journey with TRT is deeply personal and requires ongoing attention. Working closely with a knowledgeable healthcare provider is essential for achieving the right balance of hormones and minimizing side effects like gynecomastia. Regular check-ups, honest communication, and a willingness to adjust the treatment plan are all critical for success. By staying informed and proactive, men on TRT can enjoy its benefits while effectively managing any challenges that arise.
Questions and Answers
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a medical treatment used to address low testosterone levels in men. It aims to restore testosterone to normal levels, improving symptoms like fatigue, low libido, and muscle weakness.
Gynecomastia is the enlargement of male breast tissue caused by an imbalance of hormones, specifically an increase in estrogen relative to testosterone. TRT can lead to gynecomastia if excess testosterone is converted into estrogen.
Gynecomastia is relatively uncommon but can occur in men on TRT, particularly if aromatization (conversion of testosterone to estrogen) is not well managed.
Symptoms include swollen or tender breast tissue, enlargement of one or both breasts, and sometimes pain or sensitivity in the area.
TRT does not directly cause gynecomastia. It occurs if the body converts excess testosterone into estrogen, leading to a hormonal imbalance.
Preventive measures include proper dosing of testosterone, using aromatase inhibitors (AIs) to block estrogen conversion, and regularly monitoring hormone levels with blood tests.
Aromatase inhibitors, like anastrozole, reduce the conversion of testosterone to estrogen, helping to prevent or treat gynecomastia in men undergoing TRT.
Yes, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding alcohol and substances that may affect hormones, and staying active can help reduce the risk of gynecomastia during TRT.
Treatment options include adjusting the TRT dose, adding aromatase inhibitors, or in severe cases, surgical removal of the excess breast tissue.
Hormone levels should typically be monitored every 3-6 months during TRT to ensure testosterone and estrogen are balanced and to adjust treatment if needed.