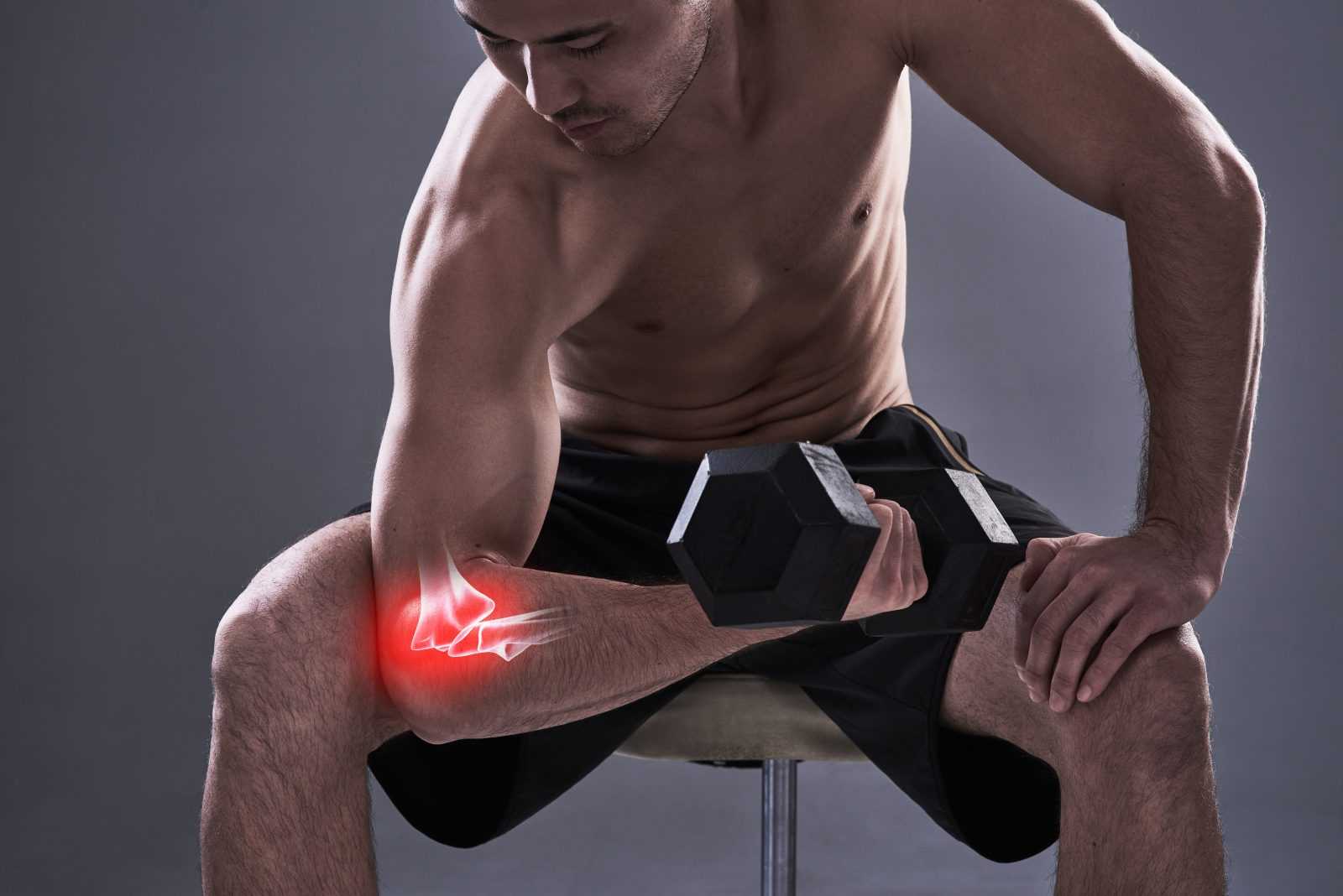
How Testosterone Can Alleviate Joint Pain: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Joint pain is a common problem that affects millions of people worldwide. It can make everyday activities difficult and reduce the quality of life. Many people seek various treatments to alleviate this pain, ranging from physical therapy to medications. One treatment that has gained attention in recent years is testosterone therapy. This article explores how testosterone can help reduce joint pain, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding its benefits, risks, and application.
Testosterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in the human body. It is often associated with male characteristics, but it is also present in females, albeit in smaller amounts. This hormone is produced in the testicles in men and the ovaries and adrenal glands in women. Testosterone is responsible for several vital functions, including the development of muscles and bones, the production of red blood cells, and the maintenance of sexual health.
In recent years, scientists and medical professionals have been exploring the link between testosterone and joint health. Joint pain can arise from various conditions, including arthritis, injuries, and wear and tear over time. Understanding how hormones like testosterone influence joint health can open new avenues for treatment and relief for those suffering from chronic pain.
One of the primary reasons this topic is gaining attention is the increasing awareness of the symptoms of low testosterone levels. These symptoms can include fatigue, decreased muscle mass, mood swings, and, notably, joint pain. By addressing low testosterone levels, it may be possible to alleviate some of these symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Testosterone therapy involves supplementing the body's natural testosterone levels through various methods such as injections, gels, patches, and implants. This therapy has shown promise in reducing joint pain by addressing one of its possible root causes: hormonal imbalance. However, it is essential to understand that testosterone therapy is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Its effectiveness can vary based on individual factors such as age, sex, overall health, and the underlying cause of joint pain.
This article will delve into the details of how testosterone therapy works, who might benefit from it, and the potential risks involved. We will also look at the different methods of administering testosterone and how to discuss this option with your healthcare provider. Furthermore, lifestyle changes that can complement testosterone therapy will be explored to provide a holistic approach to managing joint pain.
It is important to note that while testosterone therapy has potential benefits, it also comes with risks. Common side effects can include acne, sleep apnea, and an increased risk of heart disease. Long-term use of testosterone therapy requires careful monitoring by a healthcare professional to manage these risks effectively.
For those considering testosterone therapy, it is crucial to have an open and informed discussion with a doctor. This conversation should cover the potential benefits, risks, and individual suitability for the therapy. Personal medical history, current health status, and the specific nature of joint pain should all be considered when deciding whether testosterone therapy is the right choice.
In conclusion, the role of testosterone in alleviating joint pain is a topic of growing interest and research. As we continue to learn more about the complex interactions between hormones and joint health, testosterone therapy may offer a valuable option for those suffering from chronic joint pain. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding how testosterone can be used to manage joint pain, helping readers make informed decisions about their health and treatment options. By exploring the science behind testosterone and joint health, the potential benefits and risks of therapy, and practical steps for discussing this treatment with a healthcare provider, we hope to shed light on this promising avenue for pain relief.
What is Testosterone?
Testosterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in the body. It is known as the primary male sex hormone, but it is also present in females, though in smaller amounts. This section will explain what testosterone is, its biological role, how it is produced, and the normal levels found in men and women.
Definition and Biological Role of Testosterone
Testosterone is a hormone produced mainly in the testicles in men and in the ovaries and adrenal glands in women. In men, it is responsible for the development of male characteristics, such as facial hair, deep voice, and muscle mass. It also helps in producing sperm. In women, testosterone is involved in bone strength, brain function, and the development of lean muscle mass.
Hormones are chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream to tissues and organs, telling them what to do and when to do it. Testosterone belongs to a group of hormones called androgens. It affects many parts of the body, including muscles, bones, fat distribution, red blood cell production, and even mood.
Production of Testosterone in the Body
The process of producing testosterone is known as steroidogenesis. In men, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland in the brain control this process. Here’s how it works:
- Hypothalamus: This part of the brain releases a hormone called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
- Pituitary Gland: GnRH signals the pituitary gland to release luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- Testicles: LH travels to the testicles, signaling them to produce testosterone. FSH helps in the production of sperm.
In women, the ovaries produce testosterone, but in much smaller amounts. The adrenal glands, located on top of the kidneys, also produce a small amount of testosterone in both men and women.
Normal Levels of Testosterone in Men and Women
The amount of testosterone in the body is measured through blood tests. Normal levels of testosterone can vary based on age, sex, and health conditions. Here are the typical ranges:
- Men: Normal testosterone levels for adult men range from about 300 to 1,000 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL). Levels tend to be highest in the morning and decrease throughout the day.
- Women: For adult women, normal testosterone levels range from about 15 to 70 ng/dL.
Factors Affecting Testosterone Levels
Several factors can affect testosterone levels in the body, including:
- Age: Testosterone levels naturally decline with age. This is why older men often have lower testosterone levels than younger men.
- Health Conditions: Conditions like obesity, diabetes, and hormonal disorders can affect testosterone production.
- Medications: Some medications, such as steroids and opioid painkillers, can lower testosterone levels.
- Lifestyle Factors: Stress, poor diet, and lack of exercise can also impact testosterone levels.
Why Testosterone is Important
Testosterone is vital for overall health and well-being. Here are some key reasons why it is important:
- Muscle Mass and Strength: Testosterone helps build and maintain muscle mass. It also contributes to strength and endurance.
- Bone Health: It plays a crucial role in bone density. Low levels of testosterone can lead to weaker bones and increase the risk of fractures.
- Fat Distribution: Testosterone affects how the body stores fat. Low levels can lead to increased body fat, especially around the abdomen.
- Red Blood Cell Production: Testosterone stimulates the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body.
- Mood and Mental Health: It impacts mood, energy levels, and mental health. Low testosterone levels are often linked to depression, fatigue, and irritability.
Testosterone is a key hormone with many functions in both men and women. Understanding its role and maintaining healthy levels is important for overall health and quality of life.
The Connection Between Testosterone and Joint Health
Hormones are chemicals that your body makes to help control many important functions. One of these hormones is testosterone. Testosterone is mostly known for its role in male characteristics, but it is also present in females in smaller amounts. Testosterone helps with muscle strength, bone health, and mood regulation. But what about joint health?
How Hormones Impact Joint Health
Your joints are where two bones meet, allowing movement. They are surrounded by cartilage, a smooth, rubbery tissue that acts as a cushion. Hormones, including testosterone, can influence the health of these joints. Testosterone helps maintain muscle mass and bone density, which are crucial for supporting and protecting your joints.
The Mechanisms by Which Testosterone Influences Joints
There are several ways testosterone affects joint health. First, testosterone has anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammation is a natural response to injury or disease, but too much inflammation can cause pain and damage. By reducing inflammation, testosterone can help keep your joints healthier.
Second, testosterone helps build and maintain muscle mass. Strong muscles support your joints and reduce the stress on them. When your muscles are strong, your joints don’t have to work as hard, which can reduce pain and prevent injuries.
Third, testosterone supports the health of your bones. Healthy bones are essential for strong joints. Bones and joints work together to allow movement, and strong bones help protect your joints from damage.
Overview of Research on Testosterone and Joint Pain
Many studies have looked at how testosterone affects joint health and pain. Some studies show that people with low testosterone levels are more likely to have joint pain and arthritis. Arthritis is a condition that causes pain and swelling in the joints. It can make it hard to move and do everyday activities.
One study found that men with low testosterone levels had more severe arthritis in their knees compared to men with normal testosterone levels. Another study showed that women with low testosterone were more likely to have hip and knee pain.
In addition to these findings, research has also looked at testosterone therapy as a treatment for joint pain. Testosterone therapy is when a person takes additional testosterone to increase their levels. Some studies suggest that testosterone therapy can reduce joint pain and improve function in people with low testosterone levels.
Case Studies and Clinical Trials
Several clinical trials have explored the effects of testosterone therapy on joint pain. In one trial, men with low testosterone and joint pain were given testosterone injections. The results showed that their joint pain improved significantly after several months of treatment.
Another study focused on older adults with osteoarthritis, a common type of arthritis that causes the breakdown of cartilage in the joints. Participants who received testosterone therapy reported less pain and better joint function than those who did not receive the therapy.
These studies suggest a promising link between testosterone levels and joint health. However, it is important to note that more research is needed to fully understand how testosterone therapy can benefit joint health and to determine the best ways to use it.
The Bottom Line on Testosterone and Joint Health
In summary, testosterone plays a crucial role in maintaining joint health through its anti-inflammatory properties, muscle-building effects, and support for bone health. Research indicates that low testosterone levels are linked to increased joint pain and conditions like arthritis. Clinical studies show that testosterone therapy can help reduce joint pain and improve joint function, making it a potential treatment option for those with low testosterone levels.
If you are experiencing joint pain and suspect low testosterone might be a factor, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider. They can perform tests to check your hormone levels and discuss whether testosterone therapy might be right for you. Always seek professional medical advice before starting any new treatment to ensure it is safe and appropriate for your individual health needs.
Symptoms of Low Testosterone and Joint Pain
Testosterone is a vital hormone in the body, especially for men. It is mainly produced in the testicles in men and the ovaries in women, though in much smaller amounts. Testosterone plays a key role in many bodily functions, including the development of muscle mass, bone density, and the production of red blood cells. It also affects mood, energy levels, and libido.
As men age, their testosterone levels naturally decline. This is a normal part of aging, but for some, the drop can be significant, leading to a condition known as low testosterone or hypogonadism. Low testosterone can cause a variety of symptoms that can impact the quality of life.
Common Symptoms of Low Testosterone
- Fatigue: One of the most common symptoms is a persistent feeling of tiredness. Men with low testosterone often feel exhausted even after a full night’s sleep.
- Reduced Libido: Testosterone is crucial for sexual health. Low levels can lead to a decreased interest in sex, known as low libido.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Along with reduced libido, men may experience problems with erectile function. This can mean trouble getting or maintaining an erection.
- Mood Changes: Testosterone affects mood and mental health. Men with low levels may experience depression, irritability, and anxiety.
- Decreased Muscle Mass: Testosterone helps build and maintain muscle. Low levels can lead to a noticeable loss of muscle mass and strength.
- Increased Body Fat: Conversely, low testosterone can contribute to an increase in body fat, particularly around the abdomen.
- Reduced Bone Density: Testosterone helps keep bones strong. Low levels can lead to weaker bones, making them more prone to fractures.
- Cognitive Changes: Some men experience problems with memory and concentration, often referred to as "brain fog."
Understanding Joint Pain
Joint pain is a common issue affecting people of all ages. Joints are where two bones meet, allowing for movement. When there is pain in these areas, it can limit mobility and significantly affect daily activities.
Common causes of joint pain include:
- Arthritis: This is inflammation of the joints and can be due to various types such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or gout.
- Injuries: Joint pain can result from injuries like sprains, strains, or fractures.
- Overuse: Repeated use or overuse of a joint can lead to pain, commonly seen in athletes or those with physically demanding jobs.
- Infections: Certain infections can cause joint pain as a symptom.
How Low Testosterone and Joint Pain Are Connected
Interestingly, the symptoms of low testosterone and joint pain can overlap and affect each other. Here are some ways they are connected:
- Inflammation: Testosterone has anti-inflammatory properties. Low levels can increase inflammation in the body, including the joints, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Muscle and Bone Health: Low testosterone can lead to decreased muscle mass and bone density. Weaker muscles and bones can put more stress on the joints, contributing to pain.
- Fatigue and Pain Perception: Chronic fatigue from low testosterone can make joint pain feel more intense. When you are constantly tired, your body is less capable of coping with pain.
- Mood and Pain: Depression and anxiety from low testosterone can affect how you perceive and cope with pain. Poor mental health can exacerbate the experience of joint pain.
Understanding the symptoms of low testosterone and joint pain is crucial in recognizing the connection between the two. Low testosterone can significantly impact muscle mass, bone density, and inflammation levels, all of which contribute to joint health. Addressing low testosterone not only helps alleviate these symptoms but can also play a vital role in managing joint pain effectively. If you suspect you have low testosterone, consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. This comprehensive approach can improve overall well-being and quality of life.
Can Testosterone Therapy Help Alleviate Joint Pain?
Testosterone therapy is a medical treatment used to raise low levels of testosterone in the body. It can help improve many health issues. One of these issues is joint pain. In this section, we will explain what testosterone therapy is, the scientific evidence that supports it, and the risks and benefits.
What is Testosterone Therapy?
Testosterone therapy involves giving the body more testosterone. This can be done in several ways, such as:
- Injections: Testosterone is injected into the muscles. This is often done every one to two weeks.
- Gels: A gel containing testosterone is applied to the skin. The body absorbs the testosterone through the skin.
- Patches: A patch containing testosterone is placed on the skin. The testosterone enters the body through the skin.
- Implants: Small pellets containing testosterone are placed under the skin. These pellets release testosterone slowly over time.
Each method has its pros and cons. It is important to discuss with a doctor which method is best for you.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Testosterone Therapy for Joint Pain
Many studies have looked at how testosterone therapy can help with joint pain. Here are some key findings:
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Testosterone has been shown to reduce inflammation in the body. Inflammation can cause joint pain and swelling. By reducing inflammation, testosterone can help lessen joint pain.
- Cartilage Protection: Cartilage is the tissue that cushions joints. Testosterone can help protect cartilage from damage. This can help prevent joint pain and stiffness.
- Muscle Strength: Strong muscles support the joints. Testosterone can help increase muscle strength. This can take some of the pressure off the joints and reduce pain.
A review of several studies found that men with low testosterone who received testosterone therapy reported less joint pain. Another study found that older men who took testosterone had less pain and better physical function.
Risks and Benefits of Testosterone Therapy
Like any treatment, testosterone therapy has both risks and benefits. It is important to weigh these carefully.
Benefits:
- Pain Relief: Many people report less joint pain after starting testosterone therapy. This can lead to a better quality of life.
- Improved Mobility: With less pain, people can move more easily. This can make daily activities easier.
- Increased Strength: Testosterone can help build muscle. This can make the body stronger and more capable.
Risks:
- Side Effects: Common side effects include acne, hair loss, and mood changes. Some people may also experience swelling or breast enlargement.
- Long-term Risks: There may be risks to the heart and liver with long-term use. It is important to have regular check-ups with a doctor.
- Cost: Testosterone therapy can be expensive. Insurance may not always cover the cost.
Managing Risks
To manage the risks, it is important to:
- Follow the Doctor's Instructions: Always use testosterone as prescribed. Do not change the dose without talking to a doctor.
- Regular Check-ups: See a doctor regularly to monitor your health. Blood tests can check testosterone levels and look for side effects.
- Report Side Effects: If you experience any side effects, tell your doctor right away. They can help manage them.
Testosterone therapy can be an effective treatment for joint pain, especially in people with low testosterone levels. It works by reducing inflammation, protecting cartilage, and increasing muscle strength. However, it also has risks that need to be managed carefully. It is important to talk to a doctor about whether testosterone therapy is right for you. By working together with your healthcare provider, you can find the best way to manage your joint pain and improve your quality of life.
How Does Testosterone Alleviate Joint Pain?
Testosterone is a hormone that plays many important roles in the body. It is known for its influence on muscle mass, energy levels, and mood. However, testosterone also has a significant impact on joint health. This section will explain how testosterone can help reduce joint pain through various biological mechanisms.
Biological Mechanisms: Anti-inflammatory Effects
One of the main ways testosterone helps alleviate joint pain is by reducing inflammation. Inflammation is a natural response by the body to injury or infection. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can cause pain and damage to tissues, including the joints.
Testosterone has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. It can help decrease the levels of inflammatory molecules in the body. This reduction in inflammation can lead to less pain and swelling in the joints. For example, studies have found that men with higher levels of testosterone tend to have lower levels of inflammatory markers. This suggests that testosterone may help control inflammation and, as a result, reduce joint pain.
Cartilage Protection
Another way testosterone helps with joint pain is by protecting cartilage. Cartilage is a flexible tissue that covers the ends of bones in a joint. It helps reduce friction and allows the bones to move smoothly against each other. When cartilage is damaged or wears down, it can lead to pain and stiffness in the joints, a condition known as osteoarthritis.
Testosterone has been found to promote the health and repair of cartilage. It helps stimulate the production of proteins that are important for cartilage structure and function. This means that testosterone can help maintain the integrity of the cartilage, preventing it from breaking down and causing joint pain. In some studies, testosterone therapy has been shown to improve cartilage health and reduce symptoms in people with osteoarthritis.
Impact on Muscle Strength and Support for Joints
Muscle strength is crucial for joint health. Strong muscles provide better support and stability for the joints. This can help reduce the strain and pressure on the joints, which can prevent pain and injury.
Testosterone plays a key role in building and maintaining muscle mass. Higher levels of testosterone lead to greater muscle strength and size. This increased muscle mass can help support the joints more effectively, reducing the likelihood of pain and damage. For example, research has shown that testosterone therapy can increase muscle mass and strength in men with low testosterone levels. This increase in muscle strength can help alleviate joint pain by providing better support for the joints.
Studies Demonstrating Improvements in Joint Pain with Testosterone Therapy
There have been several studies that support the use of testosterone therapy for reducing joint pain. These studies provide evidence that testosterone can help improve joint health and alleviate pain.
One study looked at men with low testosterone levels and chronic joint pain. The men were given testosterone therapy for a period of several months. The researchers found that the men experienced significant reductions in joint pain and improvements in physical function. This suggests that testosterone therapy can be an effective treatment for joint pain in men with low testosterone levels.
Another study focused on older adults with osteoarthritis. The participants were given testosterone therapy and monitored for changes in their joint symptoms. The study found that testosterone therapy helped reduce pain and improve joint function in the participants. This indicates that testosterone can be beneficial for people with osteoarthritis, a common cause of joint pain.
Overall, these studies provide strong evidence that testosterone therapy can help alleviate joint pain through its anti-inflammatory effects, cartilage protection, and muscle-strengthening properties.
Testosterone helps reduce joint pain through multiple mechanisms. It decreases inflammation, protects cartilage, and strengthens muscles, all of which contribute to healthier, less painful joints. For people with low testosterone levels and joint pain, testosterone therapy may offer significant relief and improve their quality of life. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if testosterone therapy is appropriate and safe for individual needs.
Who Can Benefit from Testosterone Therapy for Joint Pain?
Testosterone therapy is a treatment option that can help reduce joint pain for some people. However, it is not suitable for everyone. This section will help you understand who might benefit from this therapy. We will look at the criteria doctors use to decide if testosterone therapy is a good choice. We will also discuss the age, sex, and health conditions that play a role in this decision.
Criteria for Considering Testosterone Therapy
Doctors use several criteria to determine if testosterone therapy might help with joint pain. Here are some of the main factors they consider:
- Low Testosterone Levels: A blood test can measure your testosterone levels. If your levels are lower than normal, you might be a candidate for testosterone therapy. Low testosterone can cause several health problems, including joint pain.
- Symptoms of Low Testosterone: Besides joint pain, other symptoms of low testosterone include fatigue, depression, low sex drive, and muscle weakness. If you have these symptoms along with joint pain, testosterone therapy might help.
- Failure of Other Treatments: If you have tried other treatments for joint pain without success, your doctor might consider testosterone therapy. This is especially true if your joint pain is severe and affects your daily life.
- Overall Health: Your overall health is important when considering testosterone therapy. If you have certain health conditions, such as prostate cancer or heart disease, testosterone therapy might not be safe for you. Your doctor will evaluate your health history before recommending this treatment.
Demographics: Age, Sex, and Health Conditions
Testosterone therapy is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Your age, sex, and health conditions can affect whether this therapy is right for you.
- Age: Testosterone levels naturally decrease with age. Men over 40 are more likely to have low testosterone levels and might benefit more from testosterone therapy. However, it can also be helpful for younger men with low testosterone due to medical conditions. Women, especially those going through menopause, might also experience low testosterone and joint pain. For them, hormone therapy could be beneficial, but it needs to be carefully managed.
- Sex: While testosterone is often associated with men, women also produce this hormone in smaller amounts. Both men and women can suffer from low testosterone levels, but the symptoms and treatment options might differ. Women considering testosterone therapy should work closely with their doctors to ensure the dosage is appropriate and to monitor any side effects.
- Health Conditions: Certain health conditions can affect testosterone levels and joint pain. For example, people with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus might have joint pain that could be alleviated by testosterone therapy. However, those with conditions such as prostate cancer, breast cancer, or severe heart problems should avoid testosterone therapy. Your doctor will review your health history to determine if testosterone therapy is safe for you.
Assessing Individual Suitability and Potential Benefits
Assessing if testosterone therapy is suitable for you involves several steps:
- Medical Evaluation: Your doctor will perform a thorough medical evaluation. This includes a physical exam, reviewing your medical history, and discussing your symptoms.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests will check your testosterone levels. These tests might be done more than once to get an accurate measurement. Your doctor might also check for other conditions that could cause your symptoms.
- Risk-Benefit Analysis: Your doctor will weigh the potential benefits of testosterone therapy against the risks. This analysis considers your age, sex, health conditions, and how much your joint pain affects your quality of life.
- Trial Period: Sometimes, doctors might suggest a trial period of testosterone therapy. This means you will take the therapy for a short time to see if it helps with your joint pain. If you notice improvement and have minimal side effects, your doctor might recommend continuing the therapy.
- Regular Monitoring: If you start testosterone therapy, regular monitoring is crucial. Your doctor will schedule follow-up appointments to check your testosterone levels and monitor any side effects. Adjustments to your treatment might be made based on these follow-ups.
Testosterone therapy can be a helpful option for reducing joint pain in people with low testosterone levels. However, it is not suitable for everyone. Factors such as age, sex, and overall health play a significant role in determining if this therapy is right for you. A thorough medical evaluation and regular monitoring are essential to ensure the safety and effectiveness of testosterone therapy. Always discuss your symptoms and treatment options with your doctor to make an informed decision.
Methods of Administering Testosterone Therapy
Testosterone therapy can be administered in several different ways. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right method depends on many factors, including personal preference, lifestyle, and medical advice. Here are the main methods of administering testosterone therapy:
Injections
How They Work:
- Testosterone injections are one of the most common forms of testosterone therapy.
- They are usually given into a muscle, often in the buttocks or thigh.
- The injections can be done at home or in a doctor's office.
Types of Injections:
- Intramuscular Injections: These are the most common type. They are given directly into the muscle, which helps the testosterone absorb quickly into the bloodstream.
- Subcutaneous Injections: These are injected under the skin and absorbed more slowly.
Frequency:
- Injections can be given weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly, depending on the specific medication and the patient's needs.
Pros:
- Injections deliver a high dose of testosterone directly into the bloodstream.
- They are effective and can be tailored to individual dosage needs.
Cons:
- Some people may find injections painful or uncomfortable.
- There can be fluctuations in testosterone levels, leading to peaks and troughs in symptoms.
Gels
How They Work:
- Testosterone gels are applied directly to the skin, usually on the shoulders, arms, or abdomen.
- The testosterone is absorbed through the skin into the bloodstream.
Types of Gels:
- Daily Gels: These are applied every day.
- Pumps: Some gels come in pump dispensers to make dosing easier.
Application:
- The gel must be applied to clean, dry skin and allowed to dry before dressing.
- It's important to wash hands after application to avoid transferring the gel to others.
Pros:
- Gels provide a steady release of testosterone throughout the day.
- They are easy to use and non-invasive.
Cons:
- There is a risk of transferring the testosterone to others through skin contact.
- Some people may experience skin irritation at the application site.
Patches
How They Work:
- Testosterone patches are applied to the skin, where they release testosterone slowly over 24 hours.
- The patches can be placed on different parts of the body, such as the back, abdomen, thighs, or upper arms.
Types of Patches:
- Daily Patches: These need to be changed every day.
- Extended-Release Patches: Some patches may be designed to last longer, but daily patches are more common.
Application:
- Patches should be applied to a clean, dry, and non-hairy area of the skin.
- It's important to rotate the application site to avoid skin irritation.
Pros:
- Patches provide a consistent level of testosterone.
- They are easy to use and do not require injections.
Cons:
- Patches can cause skin irritation or allergic reactions.
- They must be applied daily, which may be inconvenient for some users.
Implants
How They Work:
- Testosterone implants are small pellets inserted under the skin, usually in the buttocks or abdomen.
- They slowly release testosterone over several months.
Procedure:
- The insertion of the pellets is a minor surgical procedure done in a doctor's office.
- The area is numbed, and a small incision is made to place the pellets under the skin.
Duration:
- Implants can last for 3 to 6 months before they need to be replaced.
Pros:
- Implants provide a long-term, steady release of testosterone.
- They eliminate the need for daily or weekly administration.
Cons:
- The procedure to insert and remove pellets is invasive and can be uncomfortable.
- There is a risk of infection or pellet extrusion at the insertion site.
Choosing the Right Method
Choosing the right method of testosterone therapy depends on various factors. Here are some considerations:
- Lifestyle and Convenience:
- Daily gels and patches may suit individuals with a stable routine.
- Injections may be preferred by those who can manage periodic administration or visit a healthcare provider regularly.
- Implants are ideal for those seeking long-term solutions without daily maintenance.
- Medical Advice:
- Consult with a healthcare provider to understand the best option based on your health condition, testosterone levels, and response to therapy.
- Personal Preference:
- Consider comfort with needles for injections versus the convenience of gels or patches.
- Evaluate the potential for skin reactions or the hassle of daily applications.
- Side Effects and Monitoring:
- Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor testosterone levels and adjust the therapy as needed.
The method of administering testosterone therapy should be personalized to fit individual needs, preferences, and medical advice. Each method has its benefits and drawbacks, and finding the right one involves balancing effectiveness, convenience, and comfort.
Side Effects and Risks of Testosterone Therapy
Testosterone therapy can help some people with joint pain, but it also has side effects and risks. It is important to know what these are before starting treatment. This section will explain the common and rare side effects, long-term risks, and how to manage them with your doctor's help.
Common Side Effects
- Acne and Oily Skin: Many people on testosterone therapy notice that their skin becomes oilier, and they may develop acne. This happens because testosterone increases the production of oils in the skin. Using gentle skin cleansers and over-the-counter acne treatments can help manage this side effect. If acne becomes severe, a dermatologist can provide stronger treatments.
- Fluid Retention: Some people experience swelling in their lower legs and feet because their body retains more fluid. This can be uncomfortable but is usually not dangerous. Reducing salt intake and wearing compression stockings can help reduce swelling. It's important to inform your doctor if you notice significant swelling, as it could be a sign of a more serious condition.
- Increased Red Blood Cell Count: Testosterone can cause the body to produce more red blood cells. This can make the blood thicker and increase the risk of blood clots. Regular blood tests are necessary to monitor red blood cell levels. If they become too high, your doctor may adjust your dose or recommend donating blood to reduce the count.
- Mood Changes: Some people may feel more irritable or experience mood swings while on testosterone therapy. This can be challenging for both the individual and their loved ones. It's important to monitor mood changes and talk to your doctor if they become problematic. Counseling or adjustments to the therapy may help.
Rare Side Effects
- Sleep Apnea: Testosterone therapy can worsen sleep apnea, a condition where breathing stops and starts during sleep. This can lead to poor sleep quality and daytime tiredness. If you already have sleep apnea or develop symptoms like loud snoring and frequent awakenings, inform your doctor. They may refer you to a sleep specialist.
- Prostate Issues: In men, testosterone therapy can cause the prostate to grow, leading to symptoms like difficulty urinating. It may also increase the risk of prostate cancer, though this is still debated among scientists. Regular check-ups and prostate exams are important for monitoring these potential issues.
- Breast Enlargement: Some men may develop larger breasts (gynecomastia) due to hormone changes caused by testosterone therapy. This can be uncomfortable and may affect self-esteem. Surgery is an option if the enlargement is significant and bothersome.
Long-term Risks
- Heart Disease: There is some evidence that testosterone therapy might increase the risk of heart disease, especially in older men or those with pre-existing heart conditions. Symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, and unexplained fatigue should be reported to a doctor immediately. Regular cardiovascular check-ups are crucial.
- Liver Damage: Oral forms of testosterone can affect liver function. Regular blood tests can help monitor liver health. If there are signs of liver damage, such as jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), abdominal pain, or dark urine, therapy may need to be stopped or adjusted.
Monitoring and Managing Side Effects
To safely use testosterone therapy, regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is essential. This includes routine blood tests to check red blood cell levels, liver function, and hormone levels. It is also important to have regular physical exams, including prostate checks for men.
Here are some tips to help manage side effects:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help your body process the hormone and reduce the risk of fluid retention.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet can help manage side effects like acne and fluid retention. Reducing salt intake can particularly help with swelling.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can help manage mood swings and maintain overall health. It also helps with fluid retention and supports joint health.
- Follow Medical Advice: Always follow your doctor's instructions regarding dosage and frequency of testosterone administration. Do not adjust your dose without consulting your healthcare provider.
While testosterone therapy can be beneficial for alleviating joint pain, it is not without risks. Being informed about these potential side effects and working closely with your healthcare provider can help manage and mitigate these risks. Regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments play a key role in ensuring the therapy is both effective and safe.
How to Discuss Testosterone Therapy with Your Doctor
Starting a conversation about testosterone therapy with your doctor can feel daunting, but it is an essential step if you are considering it as a treatment for joint pain. Here’s a detailed guide to help you navigate this important discussion.
Preparing for the Conversation
Before you meet with your doctor, it’s helpful to do some preparation. Understanding why you’re interested in testosterone therapy and having clear questions in mind can make the conversation more productive.
- Know Your Symptoms: Keep a detailed record of your joint pain and any other symptoms you have. Note when the pain started, its severity, and any patterns you’ve noticed. Also, consider any other symptoms that might be related to low testosterone, such as fatigue, mood changes, or decreased muscle strength.
- Research Basics: Learn the basics about testosterone and its role in the body. Understand what testosterone therapy involves, including the different methods of administration. This will help you feel more confident during your discussion.
- Medical History: Be ready to discuss your full medical history, including any chronic conditions, medications, or supplements you are currently taking. Your doctor will need this information to determine if testosterone therapy is safe and appropriate for you.
What to Expect During the Appointment
When you talk to your doctor about testosterone therapy, you can expect the following steps:
- Detailed History: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. They will want to understand how your joint pain affects your daily life and if you have any other symptoms that could be linked to low testosterone.
- Physical Exam: A physical examination may be conducted to check your overall health and look for any signs that could suggest low testosterone or other health issues.
- Blood Tests: If your doctor suspects low testosterone, they will likely order blood tests to measure your hormone levels. This usually involves a simple blood draw, often done in the morning when testosterone levels are highest.
Importance of Personalized Medical Advice
Every individual is different, and what works for one person may not work for another. Your doctor’s advice will be tailored to your unique health needs. It’s important to follow their recommendations and keep an open line of communication. If you experience any side effects or if your symptoms don’t improve, let your doctor know so they can adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
Building a Partnership with Your Doctor
Think of your relationship with your doctor as a partnership. Open and honest communication is key to successful treatment. Don’t hesitate to ask questions or express any concerns you may have. Your doctor is there to help you navigate your health journey and find the best solutions for your joint pain.
Follow-Up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial when you are on testosterone therapy. These visits allow your doctor to monitor your progress, check your testosterone levels, and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment. It’s important to attend all scheduled appointments and report any changes in your symptoms.
Discussing testosterone therapy with your doctor is a critical step if you’re considering it for joint pain. By preparing in advance, asking the right questions, and maintaining open communication, you can make informed decisions about your health. Remember, personalized medical advice from your doctor is the best guide for your treatment journey.
Lifestyle Changes to Complement Testosterone Therapy
When it comes to managing joint pain, testosterone therapy can be a powerful tool. However, it’s important to remember that lifestyle changes can also make a big difference. Combining testosterone therapy with healthy habits can provide better results. This section will discuss key lifestyle changes that can help support joint health and enhance the effects of testosterone therapy.
Diet and Nutrition for Joint Health
What you eat can have a significant impact on your joints. A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients is essential for maintaining healthy joints and supporting the body’s response to testosterone therapy.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These healthy fats, found in fish like salmon and mackerel, as well as in flaxseeds and walnuts, can help reduce inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a common cause of joint pain, so including omega-3s in your diet can help alleviate some of the discomfort.
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Fruits and vegetables such as berries, spinach, and kale are high in antioxidants. These substances help protect your cells from damage and can reduce inflammation.
- Vitamin D and Calcium: These nutrients are crucial for bone health. Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium, which is necessary for strong bones and joints. You can get vitamin D from sunlight and foods like fortified milk, while calcium can be found in dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified cereals.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats can increase inflammation in the body. Try to limit your intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and fast food to help keep inflammation levels low.
Exercise and Physical Activity Recommendations
Regular physical activity is vital for maintaining joint health and supporting the effects of testosterone therapy. Exercise helps to strengthen the muscles around your joints, which can reduce the stress on these joints and decrease pain.
- Low-Impact Aerobic Exercises: Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are gentle on the joints while still providing a good workout. These exercises help improve cardiovascular health and can also help manage weight, which reduces the load on your joints.
- Strength Training: Building muscle strength can provide better support for your joints. Focus on exercises that strengthen the muscles around your joints, such as squats for your knees or shoulder presses for your shoulders. Start with light weights and gradually increase as your strength improves.
- Flexibility and Stretching: Stretching exercises like yoga and Pilates can improve your flexibility and range of motion. These activities help keep your joints limber and can prevent stiffness.
- Consistency is Key: Aim to incorporate some form of physical activity into your daily routine. Even short, regular exercise sessions can make a significant difference over time.
Stress Management and Its Impact on Hormones and Joint Health
Stress can negatively affect both your hormonal balance and joint health. High levels of stress can lead to increased inflammation and exacerbate joint pain. Managing stress effectively is therefore an important part of maintaining overall health and enhancing the benefits of testosterone therapy.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices like mindfulness meditation can help reduce stress levels. These techniques involve focusing on the present moment and can help calm your mind and reduce the production of stress hormones.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough restful sleep is crucial for managing stress and maintaining hormonal balance. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night. Good sleep hygiene, such as keeping a regular sleep schedule and creating a restful sleep environment, can help improve sleep quality.
- Relaxation Techniques: Activities like deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and even gentle activities like reading or listening to music can help lower stress levels.
- Social Support: Connecting with friends and family can provide emotional support and reduce stress. Don’t hesitate to talk to someone about what you’re going through.
By making these lifestyle changes, you can help support your joint health and maximize the benefits of testosterone therapy. Remember, it’s important to discuss any new diet, exercise, or stress management plans with your healthcare provider to ensure they’re safe and appropriate for your individual needs. Combining these healthy habits with testosterone therapy can help you manage joint pain more effectively and improve your overall quality of life.
Future Research and Developments in Testosterone Therapy for Joint Pain
The field of hormone therapy, particularly testosterone therapy, is continuously evolving. Research on the role of testosterone in alleviating joint pain is expanding, and scientists are uncovering new insights and potential treatments. This section will discuss the current gaps in research, ongoing studies, potential future therapies, and the evolving landscape of hormone therapy for joint pain.
Current Gaps in Research and Ongoing Studies
Even though testosterone therapy shows promise in alleviating joint pain, there are still many unanswered questions. One major gap in the research is understanding the long-term effects of testosterone therapy. Most studies focus on short-term outcomes, which limits our knowledge about the safety and effectiveness of testosterone over several years or decades.
Another gap is understanding how testosterone interacts with other treatments. Many people with joint pain use multiple therapies, such as pain medications, physical therapy, and dietary supplements. Researchers need to explore how testosterone therapy works in combination with these other treatments to ensure safety and maximize benefits.
Ongoing studies aim to fill these gaps. For example, some research projects are examining the long-term effects of testosterone therapy on joint health. These studies follow patients over many years to monitor changes in joint pain and overall health. Other studies are exploring how testosterone therapy interacts with different medications and lifestyle changes. These investigations will help doctors better understand how to combine treatments for the best outcomes.
Potential Future Therapies and Innovations
In the future, we may see new forms of testosterone therapy that are more effective and easier to use. Researchers are developing advanced methods for delivering testosterone, such as long-lasting injections, patches that release the hormone slowly, and even implants that can provide a steady supply of testosterone for months or years. These innovations aim to make testosterone therapy more convenient and consistent, reducing the need for frequent doctor visits and making it easier for patients to stick with their treatment plans.
Additionally, scientists are working on personalized medicine approaches. This means tailoring treatments to each person's unique biology and health needs. For example, some people may have genetic factors that affect how their bodies respond to testosterone. By understanding these factors, doctors could customize testosterone therapy to be more effective and have fewer side effects for each individual.
Another exciting area of research is the development of combination therapies. Researchers are investigating whether combining testosterone with other treatments, such as anti-inflammatory drugs or regenerative therapies, can provide better relief from joint pain. These combination therapies could address multiple aspects of joint pain, leading to more comprehensive and lasting improvements.
The Evolving Landscape of Hormone Therapy for Joint Pain
As research progresses, the landscape of hormone therapy for joint pain is likely to change significantly. One important trend is the increasing focus on holistic treatment approaches. This means considering not just the hormone levels but the overall health and well-being of the patient. For instance, lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and stress management play crucial roles in joint health and can influence the effectiveness of testosterone therapy. Future treatment plans may integrate these elements more thoroughly, offering a more balanced approach to managing joint pain.
Public awareness and understanding of testosterone therapy are also evolving. As more research becomes available and new treatments are developed, people are gaining a better understanding of how hormone therapy can help with joint pain. This increased awareness can lead to more people seeking treatment and discussing these options with their healthcare providers.
Furthermore, as new therapies emerge and existing treatments improve, the regulatory landscape will also adapt. Health authorities will need to update guidelines and approval processes to ensure that new treatments are safe and effective. This evolution in regulation will help protect patients and ensure they have access to the best possible care.
The future of testosterone therapy for joint pain is promising, with ongoing research addressing current gaps and exploring new treatment possibilities. Innovations in therapy delivery, personalized medicine, and combination treatments are set to improve the effectiveness and convenience of testosterone therapy. As the landscape of hormone therapy evolves, a holistic approach to treatment will become increasingly important, integrating lifestyle factors to enhance joint health. Public awareness and regulatory developments will continue to shape the availability and use of these therapies, ensuring safe and effective options for patients suffering from joint pain.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we've explored how testosterone can play a role in alleviating joint pain. Understanding this connection starts with knowing what testosterone is and its vital functions in the body. Testosterone is a hormone produced mainly in the testes for men and in smaller amounts in the ovaries for women. It is crucial for many bodily functions, including muscle mass, bone density, and overall energy levels.
Joint pain, a common problem for many people, can arise from various causes, including inflammation, wear and tear, and underlying health conditions. Interestingly, research has shown that low testosterone levels might contribute to joint pain. This link between testosterone and joint health is supported by numerous studies indicating that testosterone can have anti-inflammatory effects, help in maintaining cartilage, and support the muscles around the joints.
For those experiencing both low testosterone and joint pain, testosterone therapy may offer relief. Testosterone therapy involves supplementing the body's natural hormone levels through injections, gels, patches, or implants. Scientific evidence supports the idea that testosterone therapy can reduce joint pain by decreasing inflammation and improving muscle strength, which in turn supports and stabilizes the joints.
Who can benefit from testosterone therapy? Primarily, those with low testosterone levels, which can be identified through blood tests. Men over the age of 30, who naturally experience a decline in testosterone, and individuals with certain health conditions might be particularly good candidates. However, suitability for therapy should always be determined by a healthcare professional.
There are various methods to administer testosterone therapy, each with its pros and cons. Injections are effective but may require frequent doctor visits. Gels and patches are easy to apply but can cause skin irritation. Implants provide a long-term solution but involve a minor surgical procedure. It's important to choose the method that best fits one’s lifestyle and medical needs, in consultation with a doctor.
Like any medical treatment, testosterone therapy comes with potential side effects and risks. Common side effects include acne, sleep apnea, and increased red blood cell count. More serious risks, such as cardiovascular issues and prostate problems, need careful monitoring. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help manage these risks effectively.
Before starting testosterone therapy, it's crucial to have an open and honest discussion with a doctor. Being prepared with questions about the therapy's benefits, risks, and expected outcomes can help in making an informed decision. A personalized approach, tailored to individual health needs and conditions, ensures the best possible results.
Lifestyle changes can also enhance the benefits of testosterone therapy. A balanced diet rich in nutrients supports joint health. Regular exercise, particularly strength training, helps maintain muscle mass and joint stability. Managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga can positively affect hormone levels and overall joint health.
Future research in testosterone therapy for joint pain continues to evolve. Scientists are investigating new ways to optimize hormone treatments and minimize side effects. Advances in medical technology and a better understanding of hormone interactions promise exciting developments in this field. Keeping abreast of these advancements can provide new options and hope for those suffering from joint pain.
In summary, testosterone plays a significant role in maintaining joint health. For individuals with low testosterone and joint pain, therapy offers a promising treatment option. While it is essential to consider the benefits and risks, with the guidance of a healthcare provider, testosterone therapy can potentially improve quality of life by reducing joint pain and enhancing overall well-being. Always consult with a medical professional to determine the most appropriate treatment for your specific health needs. By combining medical treatments with healthy lifestyle choices, you can effectively manage joint pain and lead a more active, pain-free life.
Questions and Answers
Testosterone is a hormone primarily produced in the testicles in men and the ovaries in women. It is responsible for developing male sexual characteristics, maintaining muscle mass, bone density, and overall energy levels. In both genders, it plays a crucial role in regulating libido, mood, and even joint health.
Yes, low testosterone levels can contribute to joint pain. Testosterone helps maintain bone density and muscle mass, which are essential for joint support and function. When testosterone levels decline, it can lead to weaker bones and muscles, potentially causing joint discomfort and pain.
Testosterone helps maintain the strength and integrity of bones and muscles, which support joints. It also has anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce the risk of joint inflammation and pain. Adequate levels of testosterone help ensure that joints remain healthy and function properly.
Symptoms of low testosterone that could impact joint health include chronic fatigue, reduced muscle mass and strength, decreased bone density, and increased body fat. These factors can all contribute to joint pain and discomfort over time.
Testosterone replacement therapy can be effective in reducing joint pain, particularly in individuals with clinically low testosterone levels. TRT helps restore testosterone levels, potentially improving muscle mass, bone density, and reducing inflammation, which can alleviate joint pain.
Yes, there are risks associated with testosterone replacement therapy, including increased risk of cardiovascular events, sleep apnea, prostate issues, and blood clots. It is important to discuss these risks with a healthcare provider before starting TRT.
Yes, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a healthy diet rich in nutrients that support joint health (like omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D), maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress can help manage joint pain related to low testosterone levels.
Low testosterone is diagnosed through a blood test that measures testosterone levels. If joint pain is present, a healthcare provider may consider these levels alongside other factors such as physical examination, medical history, and imaging studies to determine the cause of the pain.
Yes, natural ways to boost testosterone levels include regular strength training, getting adequate sleep, reducing stress, maintaining a healthy weight, consuming a balanced diet with healthy fats, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption. These lifestyle changes can help improve overall testosterone levels and potentially reduce joint pain.
Yes, you should consult a doctor if you suspect your joint pain is related to low testosterone. A healthcare professional can conduct appropriate tests, diagnose any underlying issues, and recommend a treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.