Comprehensive Guide to Testosterone Injections: Benefits, Dosage, and Safety
Introduction
Testosterone is a hormone that plays a key role in the body, affecting many different functions. It is often called the "male hormone" because men have higher levels of testosterone than women. However, both men and women need testosterone for good health. This hormone helps with muscle growth, bone strength, and the production of red blood cells. It also affects mood and energy levels.
For some people, their bodies do not produce enough testosterone. This condition is called testosterone deficiency or hypogonadism. It can cause many problems, like feeling very tired, losing muscle, gaining fat, and having low sex drive. Sometimes, it can also lead to depression. To help people with low testosterone, doctors may recommend testosterone injections. These injections can help bring testosterone levels back to normal.
The purpose of this article is to give you a complete guide to testosterone injections. We will cover the benefits of these injections, how they are given, and what you need to know to use them safely. We will also talk about the possible side effects and risks, and who should not use testosterone injections.
In this article, we will start by explaining what testosterone is and why it is important. Then, we will talk about the conditions that might need testosterone therapy. After that, we will look at the benefits of testosterone injections. You will learn how these injections can help improve physical health, mental well-being, and sexual function.
Next, we will discuss how testosterone injections are given. This includes the usual dosage, how often you need to take them, and how to give yourself the injections if your doctor says it is okay to do so. We will also talk about the importance of regular check-ups and blood tests to make sure the treatment is working well and is safe for you.
We will then cover the possible side effects and risks of testosterone injections. Some side effects are common and not too serious, like pain at the injection site or acne. But there are also more serious risks, like heart problems or liver issues. It is important to know about these risks so you can talk to your doctor and make the best choice for your health.
Another important topic is who should not use testosterone injections. There are some medical conditions that make testosterone therapy unsafe. We will explain what these conditions are and why testosterone injections might not be a good idea for some people. We will also talk about possible drug interactions and precautions for specific groups of people, like older adults.
We will then give you an overview of the different testosterone products available. There are different types and brands of testosterone injections, and they are not all the same. Some are only available with a prescription, while others might be sold over the counter. Knowing the differences can help you and your doctor choose the best option for you.
Lastly, we will discuss the legal and ethical aspects of testosterone injections. The legal status of these injections can vary from place to place. There are also ethical issues to consider, like making sure the treatment is used properly and not abused. It is important to avoid misuse and follow your doctor's instructions carefully.
By the end of this article, you should have a clear understanding of testosterone injections, how they can help, and what to watch out for. Remember, it is always important to talk to your doctor before starting any new treatment. Your doctor can give you the best advice based on your specific health needs.
Testosterone injections can be a powerful tool to help people with low testosterone feel better and improve their quality of life. However, like any medical treatment, they need to be used correctly and safely. This article will help guide you through everything you need to know to make informed decisions about testosterone therapy.
Understanding Testosterone
Testosterone is a vital hormone in the human body. It is primarily known as the male sex hormone, but it is also important for women. In this section, we will explore what testosterone is, how it is produced and regulated in the body, and its various functions and importance.
What is Testosterone?
Testosterone is a hormone produced mainly in the testicles in men and in smaller amounts in the ovaries in women. It belongs to a group of hormones called androgens, which are often referred to as male hormones. However, both men and women produce and need testosterone for healthy functioning.
In men, testosterone is crucial for the development of male characteristics and reproductive functions. It helps develop the testes and prostate, increases muscle and bone mass, and promotes hair growth. In women, testosterone also plays an essential role, though in lower amounts, contributing to bone strength and the development of lean muscle mass.
Natural Production and Regulation in the Body
The production of testosterone is controlled by the brain, specifically the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Here’s how it works:
- Hypothalamus: This part of the brain produces gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). GnRH signals the pituitary gland to produce two hormones: luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- Pituitary Gland: Located at the base of the brain, the pituitary gland releases LH and FSH into the bloodstream. LH travels to the testicles in men or ovaries in women and stimulates the production of testosterone.
- Testes and Ovaries: In response to LH, the testes in men produce and release testosterone. In women, the ovaries and adrenal glands produce small amounts of testosterone.
This process is a delicate balance. The body constantly monitors testosterone levels and adjusts the production accordingly. If levels are too low, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland increase their signals to produce more. If levels are too high, these signals decrease.
Functions and Importance of Testosterone
Testosterone is essential for many body functions in both men and women. Here are some of the key roles it plays:
- Development of Male Characteristics: In men, testosterone is responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics during puberty. This includes deepening of the voice, growth of facial and body hair, and increased muscle mass and strength.
- Reproductive Functions: Testosterone is vital for sperm production in men. It also influences libido (sex drive) in both men and women. Adequate levels of testosterone ensure healthy reproductive function.
- Bone Density: Testosterone helps maintain bone density. Low levels of testosterone can lead to weak bones, increasing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis, especially in older adults.
- Muscle Mass and Strength: Testosterone promotes muscle growth and strength. It increases protein synthesis in muscle cells, which helps repair and build muscle tissue. This is why men typically have more muscle mass than women.
- Fat Distribution: Testosterone influences how the body stores fat. Men with normal testosterone levels tend to have lower body fat compared to men with low testosterone levels.
- Mood and Cognitive Function: Testosterone impacts mood and cognitive abilities. Low levels of testosterone are associated with mood swings, depression, fatigue, and decreased mental clarity. Maintaining healthy testosterone levels can improve overall mood and cognitive performance.
- Energy Levels: Testosterone contributes to overall energy levels and vitality. Men with low testosterone often experience fatigue and reduced energy, which can affect their daily activities and quality of life.
- Red Blood Cell Production: Testosterone stimulates the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Red blood cells are crucial for carrying oxygen throughout the body. Low testosterone levels can lead to anemia, a condition characterized by a lack of healthy red blood cells.
Testosterone is a critical hormone that affects many aspects of health and well-being in both men and women. Understanding how it is produced, regulated, and its various functions can help individuals recognize the importance of maintaining healthy testosterone levels for overall health.
Indications for Testosterone Injections
Testosterone injections are used to treat a variety of medical conditions where testosterone levels are abnormally low. This section explores the conditions that might require testosterone therapy, the symptoms of low testosterone, and the diagnostic criteria doctors use to determine if a patient needs testosterone injections.
Medical Conditions Requiring Testosterone Therapy
- Hypogonadism: Hypogonadism is a condition where the body doesn't produce enough testosterone. This can happen because of problems with the testicles (primary hypogonadism) or issues with the hypothalamus or pituitary gland in the brain (secondary hypogonadism). Testosterone injections are a common treatment to help bring testosterone levels back to normal.
- Delayed Puberty: Some boys do not start puberty at the usual age. This can be due to hypogonadism or other medical conditions. Testosterone injections can help stimulate the changes that occur during puberty, such as the development of secondary sexual characteristics like deepening of the voice and growth of facial hair.
- Certain Genetic Disorders: Conditions like Klinefelter syndrome, where males have an extra X chromosome, can lead to low testosterone levels. Testosterone injections can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Chronic Illnesses: Chronic conditions like HIV/AIDS and certain cancers can lead to low testosterone levels. Testosterone therapy can help improve muscle mass, strength, and mood in these patients.
- Aging-Related Low Testosterone: As men age, their testosterone levels naturally decline. Some older men experience symptoms that significantly affect their quality of life, and testosterone injections may be prescribed to help alleviate these symptoms.
Symptoms of Low Testosterone Levels
Low testosterone, or "low T," can cause a variety of symptoms that affect both physical and mental health. Some common symptoms include:
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy are common signs of low testosterone. Men with low T often feel tired even after getting enough sleep.
- Reduced Libido: Testosterone plays a key role in sex drive. Men with low testosterone often experience a reduced interest in sex.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Testosterone is important for achieving and maintaining an erection. Low levels can lead to problems with erectile function.
- Decreased Muscle Mass and Strength: Testosterone helps build muscle mass. Men with low T may notice a decrease in muscle size and strength.
- Increased Body Fat: Low testosterone can lead to an increase in body fat, particularly around the abdomen.
- Mood Changes: Low T can affect mood, leading to symptoms like depression, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
- Bone Density Loss: Testosterone helps maintain bone density. Men with low levels may be at higher risk for osteoporosis and bone fractures.
- Hair Loss: Testosterone contributes to hair growth. Men with low T may experience hair thinning or baldness.
Diagnostic Criteria for Testosterone Deficiency
Diagnosing low testosterone involves a combination of assessing symptoms and conducting blood tests to measure testosterone levels. Here are the steps doctors typically follow:
- Medical History and Physical Exam: The doctor will ask about symptoms and medical history and perform a physical examination. This helps identify potential causes of low testosterone and other health issues.
- Blood Tests: The primary test for diagnosing low testosterone is a blood test that measures the level of testosterone in the blood. This test is usually done in the morning when testosterone levels are highest. If the initial test shows low levels, the doctor may order a second test to confirm the results.
- Additional Tests: Sometimes, doctors order additional tests to determine the cause of low testosterone. These may include tests to check the levels of other hormones, such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which can help pinpoint whether the problem lies in the testicles or the brain.
- Imaging Tests: In some cases, imaging tests like MRI or CT scans may be used to check for abnormalities in the pituitary gland or hypothalamus that could be affecting testosterone production.
- Symptom Evaluation: The doctor will consider how symptoms affect the patient’s daily life. This helps in deciding whether testosterone therapy is needed.
Testosterone injections are prescribed to treat various conditions that cause low testosterone levels. Recognizing the symptoms and undergoing proper diagnostic tests are crucial steps in determining whether testosterone therapy is appropriate. If you suspect you have low testosterone, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Benefits of Testosterone Injections
Testosterone injections can provide numerous health benefits for men experiencing low testosterone levels. These benefits span physical, mental, and sexual health, significantly improving the quality of life for those affected.
Physical Health Benefits
- Increased Muscle Mass and Strength
- Testosterone plays a crucial role in muscle development. Men with low testosterone levels often experience muscle loss and weakness. Testosterone injections can help restore muscle mass and improve strength. This is particularly beneficial for those who find it difficult to build and maintain muscle despite regular exercise. Increased muscle mass not only improves physical appearance but also enhances overall body function and metabolism.
- Enhanced Bone Density
- Low testosterone levels are linked to decreased bone density, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Testosterone injections help stimulate bone mineral production, leading to stronger bones. This is especially important for older men, who are more prone to bone density loss as they age. Stronger bones reduce the risk of injuries and fractures, contributing to a more active and independent lifestyle.
- Improved Fat Distribution
- Testosterone influences how the body stores and distributes fat. Men with low testosterone often experience increased body fat, particularly around the abdomen. Testosterone injections can help reduce this fat accumulation and promote a healthier body composition. By aiding in fat distribution, testosterone therapy supports better metabolic health and reduces the risk of conditions like type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Mental Health Benefits
- Enhanced Mood and Well-being
- Low testosterone levels are often associated with mood swings, irritability, and depression. Testosterone injections can significantly improve mood and overall sense of well-being. Many men report feeling more energetic, motivated, and happier after starting testosterone therapy. Improved mood can lead to better social interactions and an overall better quality of life.
- Better Cognitive Function
- Testosterone has been linked to cognitive functions such as memory and concentration. Men with low testosterone levels may experience cognitive decline, including difficulties with memory and focus. Testosterone injections can help enhance cognitive abilities, leading to improved mental clarity and sharper thinking. This can be particularly beneficial in professional and academic settings where mental performance is crucial.
- Reduced Fatigue
- Chronic fatigue is a common symptom of low testosterone. Testosterone injections can help reduce feelings of tiredness and increase overall energy levels. This boost in energy can enhance daily activities and improve productivity. Feeling more energetic can also positively impact motivation and engagement in both personal and professional life.
Sexual Health Benefits
- Increased Libido
- One of the most well-known benefits of testosterone therapy is its impact on libido or sex drive. Men with low testosterone levels often experience a decreased interest in sex, which can affect their relationships and self-esteem. Testosterone injections can help restore sexual desire, leading to a more satisfying sex life and improved relationship quality.
- Improved Erectile Function
- Erectile dysfunction (ED) is another common issue associated with low testosterone levels. While testosterone is not the only factor involved in erectile function, adequate levels are necessary for normal erections. Testosterone injections can improve erectile function by increasing the availability of testosterone in the body. This can lead to more frequent and stronger erections, enhancing sexual performance and satisfaction.
- Better Overall Sexual Health
- In addition to increased libido and improved erectile function, testosterone therapy can positively affect other aspects of sexual health. This includes increased sperm production and improved fertility in some men. Overall, testosterone injections can contribute to a more fulfilling and active sexual life, which can have a positive impact on emotional well-being and intimate relationships.
Testosterone injections offer a wide range of benefits for men with low testosterone levels. These benefits encompass physical health improvements, such as increased muscle mass and bone density; mental health enhancements, including better mood and cognitive function; and significant positive effects on sexual health. By addressing these areas, testosterone therapy can greatly enhance the overall quality of life for those affected by low testosterone levels.
Dosage and Administration
Testosterone injections are a common treatment for men with low testosterone levels. Understanding how to use these injections properly is crucial for safety and effectiveness. This section will cover the typical dosage ranges, factors influencing dosage, administration methods, frequency of injections, and instructions for self-administration.
Typical Dosage Ranges and Factors Influencing Dosage
The dosage of testosterone injections varies depending on several factors, including age, health condition, and the severity of testosterone deficiency. Generally, doctors prescribe dosages ranging from 50 mg to 200 mg of testosterone per injection. The most common forms of testosterone used are testosterone cypionate and testosterone enanthate.
For example, a typical starting dose might be 100 mg every two weeks. However, this can be adjusted based on the patient’s response to treatment and testosterone blood levels.
Doctors will monitor testosterone levels through blood tests to ensure the dosage is effective and safe. If levels are too low, the doctor may increase the dosage. If levels are too high, the dosage may be decreased to avoid potential side effects.
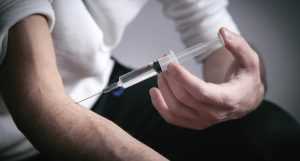
Administration Methods: Intramuscular vs. Subcutaneous
Testosterone injections can be administered in two main ways: intramuscular (IM) and subcutaneous (SC).
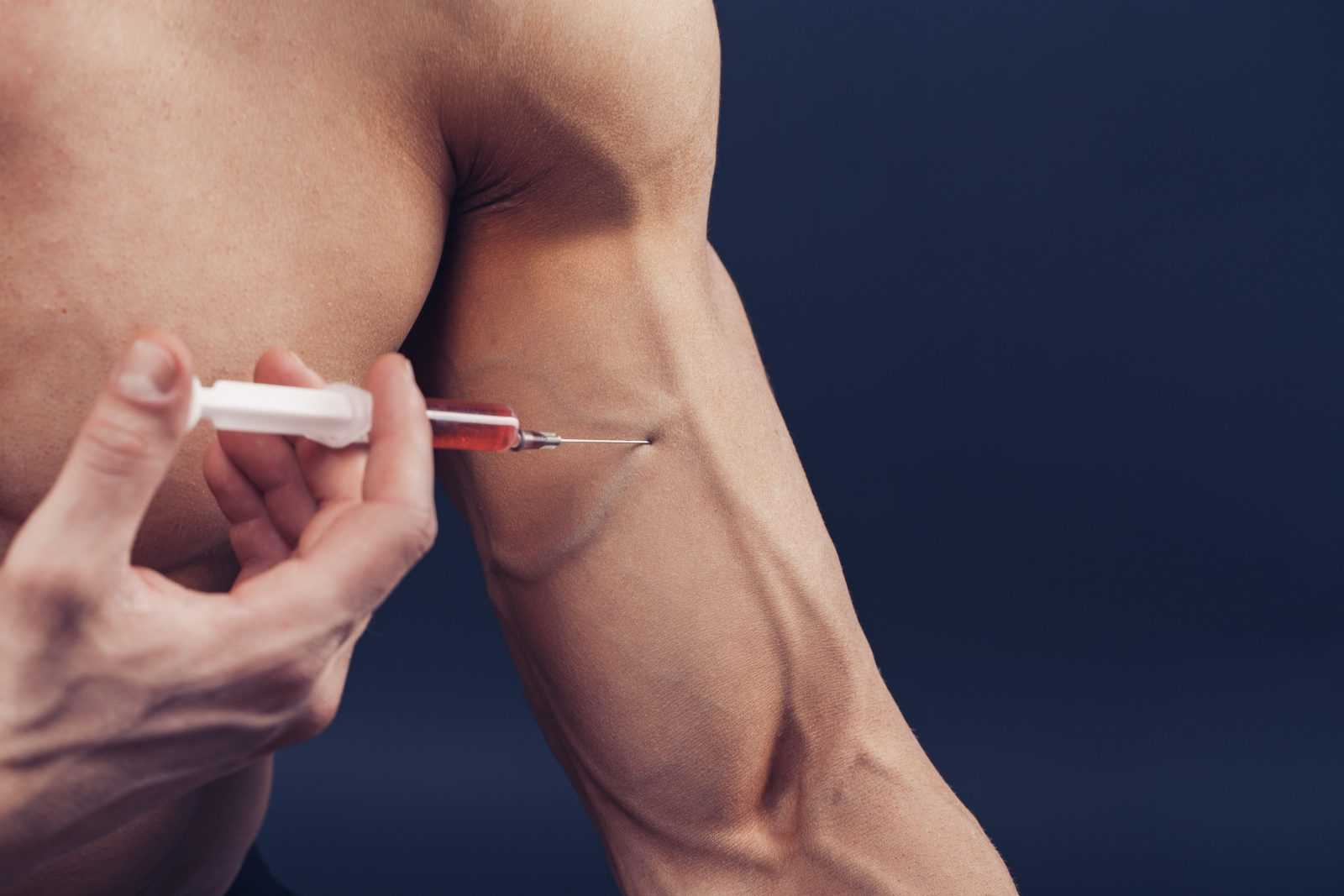
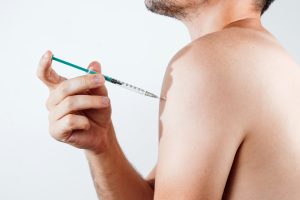
- Intramuscular (IM) Injections: These injections are given directly into a muscle. Common sites include the buttocks (gluteus muscle), thighs (quadriceps muscle), or upper arms (deltoid muscle). Intramuscular injections are the most common method and ensure that the testosterone is absorbed into the bloodstream efficiently.
- Subcutaneous (SC) Injections: These injections are given into the fat layer just under the skin. Common sites for subcutaneous injections include the abdomen or thigh. Some studies suggest that subcutaneous injections can be just as effective as intramuscular injections and may be more comfortable for some patients.
Frequency of Injections
The frequency of testosterone injections depends on the type of testosterone being used and the individual's response to treatment. Common schedules include:
- Weekly Injections: This is often recommended to maintain stable testosterone levels and avoid the peaks and troughs that can occur with less frequent dosing.
- Bi-Weekly Injections: Some patients may be prescribed injections every two weeks. This schedule may be easier to follow but can result in more significant fluctuations in testosterone levels.
Doctors may adjust the frequency based on how well the patient responds to treatment and their blood testosterone levels.
Instructions for Self-Administration
Many patients are taught to self-administer testosterone injections at home. Here are the steps involved:
- Gather Supplies: You will need a vial of testosterone, a syringe, an alcohol swab, and a disposal container for needles.
- Wash Hands: Always start by washing your hands thoroughly with soap and water to reduce the risk of infection.
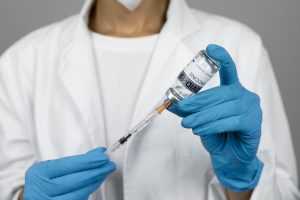
- Prepare the Injection:
- Use an alcohol swab to clean the top of the testosterone vial.
- Draw the correct dose of testosterone into the syringe. Pull back on the plunger to draw air into the syringe, then insert the needle into the vial and push the air in. This makes it easier to draw the testosterone out. Slowly pull back the plunger to draw the liquid into the syringe.
- Tap the syringe to remove air bubbles and push the plunger slightly to expel any air.
- Select Injection Site: Choose an appropriate site for injection (e.g., thigh, buttock, or abdomen for subcutaneous injections). Clean the area with an alcohol swab.
- Inject the Testosterone:
- For intramuscular injections, hold the syringe like a dart and insert it into the muscle at a 90-degree angle.
- For subcutaneous injections, pinch a fold of skin and insert the needle at a 45-degree angle.
- Push the plunger slowly to inject the testosterone.
- Dispose of Needle Safely: Place the used needle and syringe in a disposal container. Never reuse needles or syringes.
- Monitor for Side Effects: After the injection, watch for any signs of infection at the injection site (e.g., redness, swelling, pain). Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor.
Self-administration can be convenient but requires proper training and practice. It's essential to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and attend regular check-ups to monitor your testosterone levels and overall health.
Understanding the dosage and administration of testosterone injections ensures effective treatment and minimizes risks. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and adjustments to your treatment plan.
Monitoring and Adjusting Dosage
Monitoring and adjusting the dosage of testosterone injections is a critical part of ensuring effective and safe treatment. Proper monitoring helps to maximize the benefits of the therapy while minimizing potential risks and side effects. This section will discuss why regular monitoring is important, the types of blood tests used, signs that indicate a need for dosage adjustments, and the importance of working with healthcare providers.
Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring is essential for several reasons:
- Effectiveness of Treatment: Monitoring helps determine if the treatment is effective. By checking testosterone levels regularly, healthcare providers can see if the hormone levels are within the desired range.
- Safety: Monitoring ensures that testosterone levels do not become too high, which can lead to serious health risks such as heart disease, liver problems, and other complications.
- Side Effects Management: Regular check-ups allow for early detection of side effects. This helps in making timely adjustments to prevent these side effects from becoming severe.
Without regular monitoring, it is challenging to balance the benefits and risks of testosterone therapy.
Blood Tests and What They Measure
Blood tests are the primary method for monitoring testosterone therapy. These tests measure various parameters to ensure the treatment is working correctly and safely:
- Total Testosterone: This test measures the total amount of testosterone in the blood. It is usually taken in the morning when testosterone levels are highest.
- Free Testosterone: This measures the testosterone that is not bound to proteins in the blood. Free testosterone is the active form of the hormone that can enter cells and perform its functions.
- Estradiol: Testosterone can be converted into estradiol (a form of estrogen) in the body. Measuring estradiol levels helps ensure that this conversion is not excessive.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test measures various components of the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It helps detect any abnormalities caused by testosterone therapy.
- Liver Function Tests: These tests check for liver health and function, as testosterone can impact the liver.
- Lipid Profile: This test measures cholesterol levels, as testosterone can affect lipid metabolism, impacting heart health.
These tests are usually conducted before starting therapy and periodically during treatment, such as every 3 to 6 months.
Signs That Dosage Needs Adjustment
Adjusting the dosage of testosterone injections is often necessary to achieve the desired outcomes and minimize side effects. Some signs that indicate a need for dosage adjustment include:
- Persistently Low Testosterone Levels: If blood tests show that testosterone levels remain low despite treatment, the dosage may need to be increased.
- Symptoms of Low Testosterone: Ongoing symptoms such as fatigue, low libido, and depression may indicate that the current dosage is insufficient.
- High Testosterone Levels: If blood tests show testosterone levels that are too high, the dosage may need to be decreased to prevent adverse effects.
- Side Effects: New or worsening side effects, such as acne, mood swings, or sleep apnea, may require a dosage adjustment.
- Changes in Physical or Mental Health: Any significant changes in health should be discussed with a healthcare provider, as they may necessitate changes in treatment.
Working with Healthcare Providers
Collaboration with healthcare providers is crucial in managing testosterone therapy effectively. Healthcare providers play a key role in:
- Conducting Regular Tests: They will schedule and interpret the necessary blood tests to monitor treatment.
- Adjusting Dosage: Based on test results and patient feedback, providers will adjust the dosage to optimize therapy.
- Managing Side Effects: Providers offer strategies to manage and mitigate any side effects, ensuring the patient’s well-being.
- Providing Guidance: They offer valuable advice on lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, that can complement testosterone therapy.
Regular monitoring and dosage adjustments are vital components of testosterone therapy. They help ensure that the treatment is effective, safe, and tailored to the individual’s needs. Working closely with healthcare providers ensures that patients receive the best possible care and outcomes from their testosterone injections.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
Testosterone injections are used to treat men who have low testosterone levels. While these injections can help improve symptoms, they also come with potential side effects and risks. It is important to be aware of these to make informed decisions about your health. This section will explain the common side effects, serious risks, long-term safety considerations, and ways to manage and reduce side effects.
Common Side Effects
Many people who use testosterone injections experience some common side effects. These can include:
- Pain at the Injection Site: It is normal to feel some pain or discomfort where the injection was given. This pain usually goes away after a short time. Using a new needle for each injection and rotating the injection sites can help reduce pain.
- Acne and Oily Skin: Testosterone can cause the skin to produce more oil, leading to acne. Washing your face regularly and using acne treatment products can help manage this side effect.
- Mood Changes: Some people may notice changes in their mood, such as feeling more irritable or anxious. If you experience severe mood swings, it is important to talk to your doctor.
- Increased Red Blood Cell Count: Testosterone can increase the number of red blood cells in your body. While this can be a good thing for some, it can also make the blood thicker, which may increase the risk of blood clots.
Serious Risks
In addition to common side effects, there are more serious risks associated with testosterone injections. These include:
- Cardiovascular Issues: Testosterone injections may increase the risk of heart problems. Studies have shown a possible link between testosterone therapy and heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events. If you have a history of heart disease, talk to your doctor before starting testosterone injections.
- Prostate Health: Testosterone can cause the prostate gland to grow. This may lead to problems with urination or an increased risk of prostate cancer. Regular check-ups with your doctor can help monitor prostate health.
- Liver Problems: Although rare, testosterone injections can cause liver damage. Signs of liver problems include yellowing of the skin or eyes, dark urine, and abdominal pain. If you notice any of these symptoms, seek medical help immediately.
- Sleep Apnea: Testosterone can worsen sleep apnea, a condition where breathing stops and starts during sleep. If you have sleep apnea or snore loudly, discuss this with your doctor before starting treatment.
Long-Term Safety Considerations
Long-term use of testosterone injections requires careful monitoring. Some important factors to consider include:
- Bone Density: Testosterone can help increase bone density, reducing the risk of fractures. However, too much testosterone can have the opposite effect. Regular bone density tests can help ensure your bones remain healthy.
- Cholesterol Levels: Testosterone can affect cholesterol levels, potentially increasing the risk of heart disease. Monitoring cholesterol levels through blood tests is important for long-term health.
- Infertility: Testosterone injections can reduce sperm production, leading to infertility. If you plan to have children, discuss this risk with your doctor. In some cases, doctors may recommend other treatments to preserve fertility.
- Dependency and Misuse: Long-term use of testosterone can lead to dependency. Some people may misuse testosterone to enhance athletic performance or physical appearance. It is important to use testosterone only as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Managing and Mitigating Side Effects
There are several strategies to manage and reduce the side effects of testosterone injections:
- Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups with your doctor are essential. Blood tests can monitor testosterone levels, red blood cell count, liver function, and cholesterol levels. These tests help ensure the treatment is safe and effective.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage side effects. This includes eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Using the Right Dosage: Using the correct dosage is crucial. Too much testosterone can increase the risk of side effects. Always follow your doctor's instructions regarding dosage and frequency of injections.
- Open Communication with Your Doctor: Keep an open line of communication with your doctor. Report any side effects or unusual symptoms promptly. Your doctor can adjust your treatment plan as needed to improve your safety and comfort.
While testosterone injections can provide significant benefits for those with low testosterone levels, they also come with potential side effects and risks. By understanding these risks and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can manage side effects and ensure safe and effective treatment. Always follow medical advice and report any concerns to your doctor promptly.
Contraindications and Precautions
Testosterone injections can be very beneficial for people with low testosterone levels. However, not everyone can safely use this therapy. There are certain medical conditions and situations where testosterone injections are not recommended or need to be used with caution. This section will cover these contraindications and precautions in detail.
Medical Conditions That May Preclude Testosterone Therapy
- Prostate Cancer
- Testosterone can make prostate cancer grow faster. Men with prostate cancer or a history of this cancer should avoid testosterone therapy. Regular screening for prostate cancer is recommended before starting treatment.
- Breast Cancer
- Men with breast cancer should not take testosterone. Testosterone can increase the risk of breast cancer cells growing and spreading.
- Severe Sleep Apnea
- Testosterone therapy can make sleep apnea worse. Sleep apnea is a condition where breathing stops and starts during sleep. It can lead to serious health problems if not treated properly.
- Severe Heart Conditions
- Men with serious heart problems, such as uncontrolled heart failure, should avoid testosterone therapy. Testosterone can increase the risk of heart attack and other cardiovascular issues.
- Polycythemia
- This is a condition where the blood becomes too thick due to too many red blood cells. Testosterone can increase the number of red blood cells, making the condition worse.
- Severe Liver or Kidney Disease
- Men with serious liver or kidney problems need to be cautious. Testosterone is processed by the liver and kidneys. If these organs are not working well, testosterone therapy can cause more harm.
Drug Interactions
Testosterone can interact with other medications. These interactions can reduce the effectiveness of testosterone or the other medications. They can also increase the risk of side effects. Some common drug interactions include:
- Blood Thinners (Anticoagulants)
- Testosterone can increase the effects of blood thinners. This can lead to a higher risk of bleeding.
- Insulin and Diabetes Medications
- Testosterone can affect blood sugar levels. Men taking insulin or other diabetes medications may need to adjust their doses.
- Corticosteroids
- These drugs can increase the risk of fluid retention when taken with testosterone. This can be especially dangerous for men with heart or kidney problems.
- Propranolol
- This is a medication used for high blood pressure and other heart conditions. Testosterone can change how the body responds to propranolol.
Precautions for Specific Populations
- Elderly Men
- Older men are more likely to have prostate problems, heart disease, and other conditions that make testosterone therapy risky. They need careful screening and monitoring.
- Young Adults and Teenagers
- Testosterone therapy can affect bone growth and development in young people. It should be used with caution in this age group and only under the guidance of a specialist.
- Men Planning to Have Children
- Testosterone therapy can reduce sperm production and fertility. Men who want to have children should discuss this with their doctor before starting treatment.
- Women
- Testosterone therapy is sometimes used in women for certain medical conditions. However, it can cause side effects like deepening of the voice, hair growth, and other changes. Women should use testosterone only under the guidance of a doctor.
Regular Monitoring
Men on testosterone therapy need regular monitoring. This includes:
- Blood Tests
- Regular blood tests are necessary to check testosterone levels, red blood cell count, liver function, and other important markers.
- Prostate Checks
- Regular prostate exams and PSA (prostate-specific antigen) tests are essential to monitor prostate health.
- Heart Health
- Monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall heart health is important, especially for men with a history of heart disease.
- Sleep Studies
- Men with or at risk for sleep apnea may need sleep studies to monitor their condition while on testosterone therapy.
Testosterone injections can be a valuable treatment for men with low testosterone levels, but they are not suitable for everyone. Men considering this therapy should discuss their full medical history with their doctor. They should also understand the potential risks and the need for ongoing monitoring to ensure the treatment is safe and effective for them. By taking these precautions, men can make informed decisions about their health and testosterone therapy.
Testosterone Injection Products
Testosterone injection products come in various forms and brands, each designed to suit different needs and preferences. Understanding the options available can help you and your healthcare provider choose the best one for your treatment.
Overview of Different Testosterone Formulations
There are several formulations of testosterone injections, each with unique characteristics. The most common forms include:
- Testosterone Cypionate: This is one of the most popular forms of testosterone injections. It is known for its long-lasting effects, typically requiring administration every one to two weeks. The slow release of testosterone cypionate helps maintain steady hormone levels in the body.
- Testosterone Enanthate: Similar to testosterone cypionate, testosterone enanthate is also a long-acting form of testosterone. It is usually administered every one to two weeks. This formulation is widely used and is often prescribed for its reliable and steady effects.
- Testosterone Propionate: This formulation has a shorter half-life compared to cypionate and enanthate. It needs to be injected more frequently, typically every two to three days. While it provides quicker results, the frequent injections can be a drawback for some patients.
- Testosterone Undecanoate: This is a very long-acting form of testosterone that can last up to ten weeks per injection. It is less commonly used due to its extended duration and the higher dosage required. However, it is a good option for those who prefer less frequent injections.
- Combination Formulations: Some products combine different esters of testosterone to provide both immediate and long-lasting effects. These formulations aim to offer the benefits of both short and long-acting testosterone injections.
Comparing Brands and Types of Injections
There are various brands of testosterone injections available, each with slight differences in formulation and administration. Here are a few commonly prescribed brands:
- Depo-Testosterone: This brand of testosterone cypionate is widely used due to its effectiveness and availability. It is administered via intramuscular injection, typically into the buttocks.
- Delatestryl: This is a brand of testosterone enanthate. Like Depo-Testosterone, it is injected into the muscle and is known for its reliable results in maintaining testosterone levels.
- Testoviron Depot: This brand combines testosterone enanthate and testosterone propionate, offering both immediate and prolonged effects. It is favored by some for its balanced release profile.
- Nebido: This is a brand of testosterone undecanoate, known for its very long duration of action. It is administered less frequently, making it a convenient option for those who prefer fewer injections.
When choosing a brand or type of injection, consider factors such as the frequency of injections, cost, availability, and your body's response to the treatment. Your healthcare provider can help you decide which product is best suited to your needs.
Prescription vs. Over-the-Counter Products
Testosterone injections are generally available only with a prescription. This ensures that the treatment is appropriate for your medical condition and is monitored by a healthcare professional. Over-the-counter testosterone products, such as supplements and gels, are not the same as prescription injections and may not be effective for treating low testosterone levels.
Prescription testosterone injections are regulated to ensure safety and efficacy. They are prescribed based on a thorough evaluation of your symptoms, blood tests, and overall health. Self-medicating with over-the-counter products can be risky and is not recommended.
Importance of Medical Supervision
Using testosterone injections without medical supervision can lead to serious health risks. A healthcare provider will monitor your treatment to ensure the dosage is correct, manage any side effects, and adjust the treatment as needed. Regular blood tests are essential to track your hormone levels and overall health.
Testosterone injection products come in various forms and brands, each with unique benefits and considerations. It is crucial to work with your healthcare provider to choose the right formulation and ensure safe and effective treatment. Avoid over-the-counter products and self-medication to prevent health risks and ensure optimal results from your testosterone therapy.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Testosterone injections are a medical treatment that can improve the quality of life for many people with low testosterone levels. However, it is essential to understand the legal and ethical considerations associated with their use. This section will cover the legal status of testosterone injections, ethical considerations in prescribing and using them, and how to avoid misuse and abuse.
Legal Status of Testosterone Injections
The legal status of testosterone injections varies by country and region. In many places, testosterone is classified as a controlled substance. This means it is regulated by the government due to its potential for abuse and health risks.
In the United States, for example, testosterone is classified as a Schedule III controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act. This means that it is illegal to possess or distribute testosterone without a valid prescription from a licensed healthcare provider. Doctors can prescribe testosterone injections to patients who have been diagnosed with conditions like hypogonadism, where the body does not produce enough testosterone naturally.
Other countries have similar regulations. In the United Kingdom, testosterone is a prescription-only medication. In Australia, it is also classified as a controlled substance and requires a prescription. These laws are in place to ensure that testosterone is used safely and appropriately.
Ethical Considerations in Prescribing and Using Testosterone
Prescribing testosterone injections involves several ethical considerations for healthcare providers. Doctors must ensure that they are prescribing testosterone for legitimate medical reasons and not for performance enhancement or other non-medical uses.
Proper Diagnosis and Indications: Before prescribing testosterone, healthcare providers should conduct a thorough evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and blood tests to confirm low testosterone levels. Prescribing testosterone without proper diagnosis can lead to unnecessary risks and health complications.
Informed Consent: Patients should be fully informed about the potential benefits and risks of testosterone therapy. This includes discussing possible side effects, long-term health implications, and the need for regular monitoring. Informed consent ensures that patients are making educated decisions about their treatment.
Avoiding Conflicts of Interest: Healthcare providers should avoid any conflicts of interest that could influence their prescribing practices. For instance, they should not prescribe testosterone to profit financially from its sale or to meet patient demands without medical justification.
Patient Monitoring and Follow-Up: Ethical prescribing also involves regular monitoring of patients on testosterone therapy. This includes periodic blood tests to check testosterone levels and assess for side effects. Ongoing follow-up helps ensure that the treatment remains safe and effective.
Avoiding Misuse and Abuse
Testosterone injections have the potential for misuse and abuse, particularly among individuals seeking to enhance athletic performance or physical appearance. Misuse can lead to serious health risks, including cardiovascular problems, liver damage, and psychological effects.
Education and Awareness: Patients should be educated about the risks of using testosterone without medical supervision. They should understand that using testosterone for purposes other than those prescribed by a healthcare provider can have dangerous consequences.
Secure Storage and Disposal: To prevent misuse, testosterone injections should be stored securely and disposed of properly. Patients should keep their medication in a safe place and follow guidelines for disposing of needles and unused medication.
Addressing Suspected Abuse: Healthcare providers should be vigilant for signs of testosterone abuse among their patients. This includes monitoring for unusual patterns of use, such as requests for higher doses or more frequent prescriptions. If abuse is suspected, doctors should address the issue with the patient and consider involving addiction specialists if necessary.
Regulatory Compliance: Both patients and healthcare providers must comply with legal regulations regarding the use and distribution of testosterone. This includes ensuring that prescriptions are legitimate and that any use of testosterone is under the supervision of a licensed healthcare provider.
Understanding the legal and ethical considerations of testosterone injections is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. Ensuring that testosterone is used safely, appropriately, and ethically can help maximize its benefits while minimizing risks. Patients should always seek treatment from qualified healthcare professionals and adhere to prescribed guidelines to avoid misuse and abuse. By doing so, they can achieve the best possible outcomes from their testosterone therapy.
Conclusion
Testosterone injections are an important treatment for people with low testosterone levels. This guide has explored many aspects of testosterone injections, from what testosterone is to the benefits, risks, and legal considerations of using this therapy. Understanding these points can help individuals make informed decisions about their health.
Testosterone is a crucial hormone in the body. It affects many functions, including muscle mass, bone density, mood, and sexual health. When testosterone levels are low, people can experience a range of symptoms such as fatigue, depression, and decreased libido. Testosterone injections help restore normal levels, improving these symptoms and overall well-being.
The benefits of testosterone injections are significant. They can lead to increased muscle mass, better bone density, and improved mood. These injections also enhance sexual health by boosting libido and improving erectile function. Many people also report better energy levels and cognitive function after starting testosterone therapy. These benefits can greatly improve quality of life for those with low testosterone levels.
Dosage and administration of testosterone injections are important to get right. The typical dosage depends on various factors, including age, weight, and the severity of testosterone deficiency. Injections can be given intramuscularly (into the muscle) or subcutaneously (under the skin). The frequency of injections varies, but they are often administered every one to two weeks. It is essential to follow the instructions provided by healthcare providers to ensure the treatment is effective and safe.
Regular monitoring and dosage adjustment are crucial parts of testosterone therapy. Blood tests are needed to measure testosterone levels and ensure they are within the desired range. These tests also help detect any potential side effects early. Signs that dosage may need adjustment include changes in mood, energy levels, or physical symptoms. Healthcare providers play a vital role in monitoring patients and making necessary adjustments to optimize treatment outcomes.
Like any medical treatment, testosterone injections come with potential side effects and risks. Common side effects include pain at the injection site, acne, and increased red blood cell count. More serious risks involve cardiovascular issues, such as heart attacks and strokes, and liver problems. Long-term safety considerations are also important, as prolonged use of testosterone can impact various organs and systems in the body. It is crucial to discuss these risks with a healthcare provider and to manage any side effects that arise during treatment.
Certain medical conditions may preclude the use of testosterone therapy. For example, men with prostate or breast cancer should avoid testosterone injections. Additionally, people with severe heart, liver, or kidney disease need to exercise caution. Drug interactions are another important consideration, as testosterone can interact with other medications. Precautions are particularly necessary for specific populations like the elderly and young adults. These groups may be more susceptible to the effects of testosterone and require careful monitoring.
There are various testosterone injection products available. These include different formulations and brands, each with its own characteristics. Some products are designed for intramuscular injection, while others are for subcutaneous use. It is important to use a product that is prescribed by a healthcare provider and to avoid over-the-counter options that may not be safe or effective.
Legal and ethical considerations also play a role in testosterone therapy. The legal status of testosterone injections varies by region, with some areas having stricter regulations than others. Ethical considerations include ensuring that testosterone is prescribed appropriately and not misused. Misuse and abuse of testosterone can lead to serious health problems and legal issues. It is important to follow medical advice and use testosterone responsibly.
In summary, testosterone injections offer significant benefits for individuals with low testosterone levels. They can improve physical, mental, and sexual health. However, it is important to understand the dosage, administration, monitoring, and potential risks associated with this therapy. Legal and ethical considerations should also be taken into account. By working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can use testosterone injections safely and effectively to improve their quality of life.
Questions and Answers
Testosterone injection is used to treat conditions caused by a lack of testosterone in the body, such as hypogonadism in men. It helps restore normal testosterone levels, improving symptoms like low sex drive, fatigue, and muscle weakness.
Testosterone injection is typically administered intramuscularly, meaning it is injected into a muscle. Common sites include the gluteus (buttocks) and deltoid (shoulder) muscles. It can be given by a healthcare professional or self-administered with proper training.
Common side effects include pain or swelling at the injection site, headache, dizziness, mood changes, and increased red blood cell count. Some individuals may also experience acne, hair loss, or changes in libido.
The frequency of testosterone injections depends on the specific formulation and individual patient needs. Commonly, injections are given every 1 to 4 weeks. Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate schedule for you.
Yes, testosterone injections can affect fertility. High levels of testosterone can suppress sperm production, potentially leading to reduced fertility. It is important to discuss fertility plans with your healthcare provider before starting treatment.
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and resume your regular schedule. Do not double the dose to catch up. Consult your healthcare provider for specific instructions.
Yes, testosterone injections are contraindicated in individuals with prostate cancer, breast cancer, severe heart, liver, or kidney disease, and certain other conditions. Always disclose your full medical history to your healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Testosterone injections are generally not recommended for women except in certain cases under strict medical supervision, such as for the treatment of gender dysphoria or specific hormone imbalances. High levels of testosterone in women can cause virilization.
Testosterone injections should be stored at room temperature, away from light and moisture. Keep them out of reach of children and do not freeze. Follow the specific storage instructions provided with your medication.
While some athletes and bodybuilders misuse testosterone injections to enhance performance or muscle mass, this practice is illegal and can have serious health risks, including heart disease, liver damage, and psychological effects. Use testosterone only under medical supervision for approved indications.