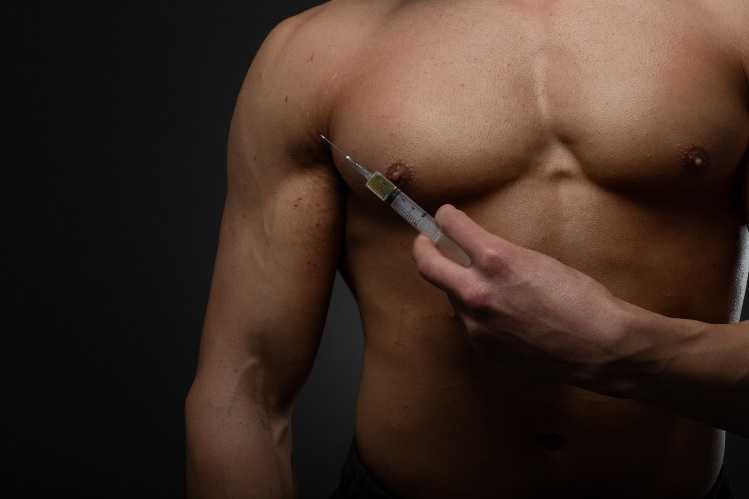
What are testosterone therapy shots?
Testosterone therapy shots, also known as testosterone injections, are a form of hormone replacement therapy predominantly used to treat men diagnosed with low testosterone levels, a condition medically referred to as hypogonadism. Testosterone is a crucial hormone in men, playing a vital role in muscle mass, bone density, red blood cell production, sexual function, and overall emotional health. When the body doesn’t produce sufficient amounts of testosterone, it can lead to various physical and psychological symptoms, including decreased libido, fatigue, weight gain, depression, and decreased bone density.
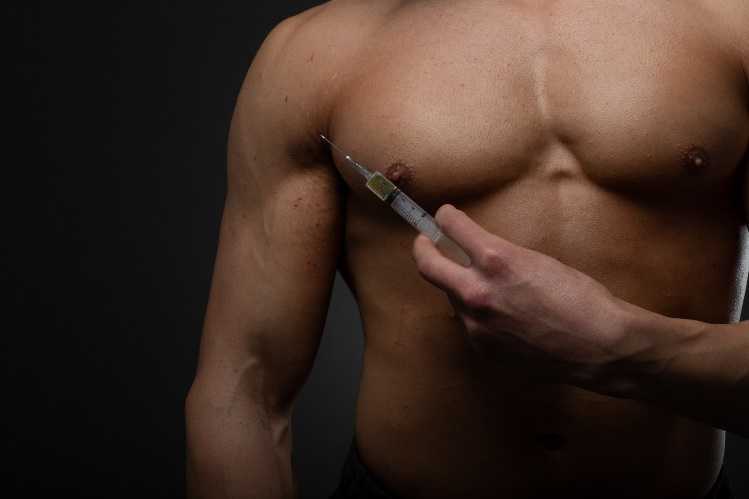
The process of administering testosterone therapy involves intramuscular injections, which allow the hormone to be directly absorbed into the bloodstream. These injections are typically given by a healthcare professional in a clinic, though some patients may be taught to administer the shots themselves at home. The frequency of these injections can vary widely depending on the individual's specific health needs and the form of testosterone used. Commonly, injections are given every two to four weeks.
There are several types of testosterone formulations used in these injections, including testosterone cypionate, testosterone enanthate, and testosterone propionate. Each of these has different characteristics in terms of how quickly they are absorbed by the body and how long their effects last. The choice of formulation often depends on the patient's response to therapy, their health history, and their personal preference, in consultation with their healthcare provider.
Testosterone therapy aims to restore testosterone levels to a normal range, thereby alleviating the symptoms associated with low testosterone. However, it’s important to note that testosterone therapy is not suitable for all individuals. It is specifically designed for those with clinically diagnosed hypogonadism and not for men experiencing the natural decrease in testosterone production that comes with aging, unless they exhibit symptoms of low testosterone that affect their quality of life.
See also low t center near me.
The decision to start testosterone therapy should be based on a thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and blood tests to measure testosterone levels. It is crucial for patients to understand that while testosterone therapy can offer significant benefits in terms of energy, mood, and sexual function, it also comes with potential risks and side effects that need to be considered and discussed with a healthcare professional.
Testosterone therapy shots are a powerful tool in the management of hypogonadism, offering hope and improved quality of life to many men suffering from low testosterone levels. However, like any medical treatment, they require careful consideration and monitoring to maximize benefits and minimize risks.
Who Needs Testosterone Therapy Shots?
Testosterone therapy shots are specifically designed for individuals diagnosed with hypogonadism, a medical condition characterized by insufficient production of testosterone. Testosterone, a hormone critical for male health and well-being, influences various bodily functions, including muscle mass and strength, bone density, fat distribution, red blood cell production, sexual function, and fertility. When levels fall below the normal range, it can lead to significant physical, emotional, and psychological effects.
Identifying Candidates for Testosterone Therapy
The primary candidates for testosterone therapy are men who have clinical symptoms of low testosterone and have been confirmed to have low levels through blood tests. Symptoms of low testosterone can vary widely but often include:
- Reduced libido or sexual desire
- Erectile dysfunction
- Decreased muscle mass and strength
- Increased body fat
- Reduced bone density, increasing the risk of osteoporosis
- Fatigue and lack of energy
- Mood swings, depression, or irritability
- Decreased body hair
- Concentration and memory problems
However, it's crucial to note that these symptoms can also be associated with other health conditions. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is necessary to rule out other potential causes and confirm that low testosterone is the underlying issue.
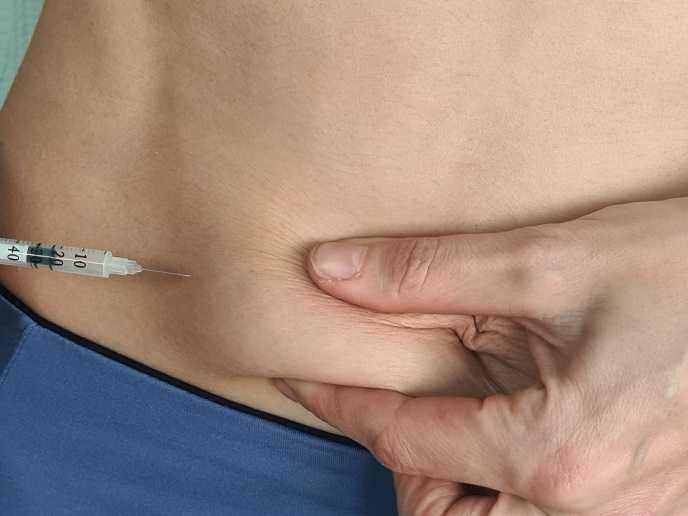
Age-Related Decline in Testosterone
While online testosterone therapy is most commonly associated with treating hypogonadism, there's growing interest in its use for age-related declines in testosterone, often referred to as "late-onset hypogonadism" or "andropause." As men age, it's natural for testosterone levels to decrease gradually. This decline can exacerbate or lead to symptoms similar to those of hypogonadism. However, the decision to treat age-related decreases in testosterone with therapy is more complex and requires careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks.
Evaluating the Need for Therapy
Determining the need for testosterone therapy involves more than just identifying symptoms. It requires:
- Blood Tests: Multiple measurements of testosterone levels, typically performed in the morning when levels are highest, are necessary to accurately assess deficiency.
- Assessment of Symptoms: A detailed medical history and physical examination to evaluate symptoms and their impact on quality of life.
- Consideration of Overall Health: Evaluating the patient's overall health, including potential risks and contraindications for therapy, such as history of prostate or breast cancer, untreated sleep apnea, severe urinary tract symptoms, or heart failure.
Testosterone therapy shots are a targeted treatment for men diagnosed with hypogonadism, offering potential relief from its various symptomatic burdens. However, the decision to pursue testosterone therapy must be grounded in a comprehensive evaluation and collaborative discussion between the patient and healthcare provider, considering the individual's specific symptoms, testosterone levels, overall health, and treatment goals. This personalized approach ensures that those who stand to benefit most from therapy are identified and treated appropriately, while minimizing unnecessary risks for those for whom therapy might not be suitable.
What are the benefits of testosterone therapy shots?
The administration of testosterone therapy shots has been associated with a range of potential benefits, especially for men diagnosed with hypogonadism or significantly low levels of testosterone. These benefits span across various aspects of physical and psychological health, contributing to an improved quality of life for many individuals undergoing treatment.
One of the most immediate and noticeable benefits of testosterone therapy is the improvement in sexual function. This includes increased libido, better erectile function, and in some cases, increased sexual satisfaction. These changes can significantly impact an individual's relationship and overall sense of well-being.
Beyond sexual health, testosterone therapy can also contribute to physical health improvements. Increased muscle mass and strength are common outcomes, making the therapy particularly beneficial for those experiencing muscle wasting or weakness. This is coupled with a potential reduction in body fat, particularly in the abdominal area, which is crucial for overall cardiovascular health. Furthermore, testosterone plays a vital role in bone density. Therapy can help in preventing osteoporosis or reducing the risk of fractures by strengthening the bones.
From a psychological perspective, testosterone therapy can lead to improvements in mood, energy levels, and sense of vitality. Men undergoing therapy often report a decrease in feelings of depression and fatigue, which in turn can lead to a more active and engaged lifestyle. This boost in mood and energy can have a cascading positive effect on personal relationships, work performance, and general life satisfaction.
Additionally, there are indications that testosterone therapy can improve cognitive functions. Some studies suggest improvements in memory, focus, and concentration, although the research in this area is ongoing and conclusions are more tentative.
It's important to highlight that the degree to which these benefits are experienced can vary widely among individuals. Factors such as age, baseline testosterone levels, the presence of other medical conditions, and lifestyle choices can all influence the outcomes of therapy. Moreover, achieving these benefits requires careful monitoring and adjustment of testosterone levels to avoid overshooting to abnormally high levels, which can negate the positive effects or introduce risks.
What are the risks and side effects?
While testosterone therapy can offer significant benefits, it is not without its potential risks and side effects. These must be carefully weighed against the advantages, especially considering the individual health profile and needs of each patient.
One of the most discussed risks is the potential for cardiovascular problems. Research has shown mixed results, with some studies suggesting an increased risk of heart attacks and strokes associated with testosterone therapy, especially in older men or those with pre-existing heart conditions. However, other studies have not found a significant link, indicating the need for further research and personalized assessment by healthcare providers.
Another significant concern is the association between testosterone therapy and prostate health. Testosterone can stimulate the growth of prostate tissue, leading to concerns about the potential increase in the risk of prostate cancer. While current evidence does not conclusively show that testosterone therapy raises the risk of developing prostate cancer, it may accelerate the growth of existing prostate cancer or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Regular monitoring of prostate health through PSA (prostate-specific antigen) tests and digital rectal exams is recommended for men undergoing testosterone therapy.
Testosterone therapy can also lead to a range of other side effects, including but not limited to, acne and oily skin, sleep apnea (especially in overweight individuals or those with pre-existing conditions), polycythemia (an increase in red blood cell count, which can increase the risk of blood clots), and breast enlargement or tenderness. Some men may experience mood swings or aggression, although these are less common and often associated with supra-physiological levels of testosterone.
Fertility concerns are also notable, as testosterone therapy can suppress sperm production, potentially leading to temporary infertility. Men wishing to father children should discuss alternative treatments or sperm preservation methods with their healthcare provider before starting therapy.
Finally, the possibility of liver toxicity, though rare with injections compared to oral formulations of testosterone, and fluid retention, leading to edema, are also concerns that need monitoring during therapy.
It's crucial for individuals considering testosterone therapy to engage in a thorough discussion with their healthcare provider about these risks and side effects. A careful evaluation of the patient's health history, current health status, and specific needs can help in making an informed decision about whether the benefits of testosterone therapy outweigh the potential risks. Regular monitoring throughout the treatment process is essential to ensure safety and adjust the therapy as needed.
How long does it take to see results?
The timeline for experiencing the benefits of testosterone therapy can vary significantly among individuals, influenced by factors such as the severity of testosterone deficiency, the dosage of testosterone administered, and the individual’s overall health and lifestyle. Generally, patients may begin to notice improvements in certain symptoms within a few weeks, but it often takes longer for the full range of benefits to manifest.
Initial changes that may be observed include an increase in sexual desire and improvements in mood and energy levels, often reported within the first month of therapy. These early improvements are particularly encouraging for patients, as they provide immediate feedback that the treatment is beginning to take effect.
Physical changes, such as increased muscle mass and a reduction in fat mass, typically require more time, often becoming noticeable after several months of consistent treatment. Similarly, improvements in bone density, which can play a crucial role in preventing osteoporosis, might only be detectable on bone density scans after 6 months to a year of therapy.
Cognitive improvements and further enhancements in mood and energy can also continue to evolve over the first few months. It is important for patients to have realistic expectations and understand that achieving the full benefits of testosterone therapy is a gradual process that requires patience and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan.
Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential during this period to monitor the patient’s response to treatment, adjust dosages as necessary, and ensure that testosterone levels are maintained within a healthy range. These check-ins also provide an opportunity to assess and manage any side effects that may arise, ensuring that the benefits of therapy continue to outweigh any potential risks.
How are testosterone levels monitored during therapy?
Monitoring testosterone levels during therapy is critical to ensure that patients are receiving an optimal dose that alleviates symptoms of testosterone deficiency without leading to excessive levels that could increase the risk of side effects. The process typically involves regular blood tests to measure the concentration of testosterone in the patient’s bloodstream.
At the start of therapy, blood tests may be conducted more frequently, such as every few weeks to months, to closely monitor the patient’s response to treatment and adjust the dosage as needed. Once a stable and effective dose is established, the frequency of testing may decrease to every 3 to 6 months.
These tests are usually conducted in the morning when testosterone levels are at their highest. This helps in accurately assessing the effectiveness of the therapy and making necessary adjustments. In addition to measuring total testosterone levels, healthcare providers may also monitor levels of other hormones, such as estrogen and luteinizing hormone (LH), and assess markers of prostate health, blood counts, and lipid profiles to ensure the therapy is not adversely affecting the patient’s overall health.
Effective monitoring also involves regular check-ins with the patient to discuss their symptoms, any side effects they are experiencing, and their satisfaction with the treatment. This holistic approach ensures that adjustments to the therapy can be made based on a comprehensive understanding of its impact on the patient’s health and well-being.
Both sections 5 and 6 highlight the individualized nature of testosterone therapy and the importance of ongoing communication and collaboration between the patient and healthcare provider to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Can testosterone therapy help with erectile dysfunction?
Testosterone therapy has been recognized as a potential treatment for erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with low testosterone levels. ED is a condition where a man has difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection suitable for sexual intercourse, and it can have significant psychological and relationship impacts. Since testosterone plays a crucial role in sexual function, addressing low levels through therapy can improve ED symptoms for some men.
The relationship between testosterone and erectile function is complex and involves multiple physiological processes. Testosterone is responsible for the normal growth and development of male sex organs and for maintenance of secondary sex characteristics, including the modulation of libido and the maintenance of erectile function. Low levels of testosterone can lead to a decrease in libido and changes in erectile function, making testosterone therapy a viable treatment option.
It's important to note, however, that testosterone therapy is most effective for ED in the context of low testosterone levels. Men with ED but normal testosterone levels are unlikely to see an improvement in erectile function with testosterone therapy alone and may require other treatments for ED, such as phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil, tadalafil).
The effectiveness of testosterone therapy for ED can vary, with some men experiencing significant improvements in erectile function and libido, while others may notice only a modest benefit. This variability can be attributed to the multifactorial nature of ED, where psychological factors, vascular health, and other hormones also play critical roles.
Before starting testosterone therapy for ED, it is essential for patients to undergo a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider to confirm low testosterone levels and to assess for other potential causes of ED. This evaluation should include a detailed medical and sexual history, a physical examination, and appropriate laboratory tests.
Is testosterone therapy safe for aging men?
The use of testosterone therapy in aging men, often seeking to alleviate symptoms associated with andropause or "male menopause," such as decreased libido, fatigue, loss of muscle mass, and cognitive decline, has been a subject of considerable debate and research.
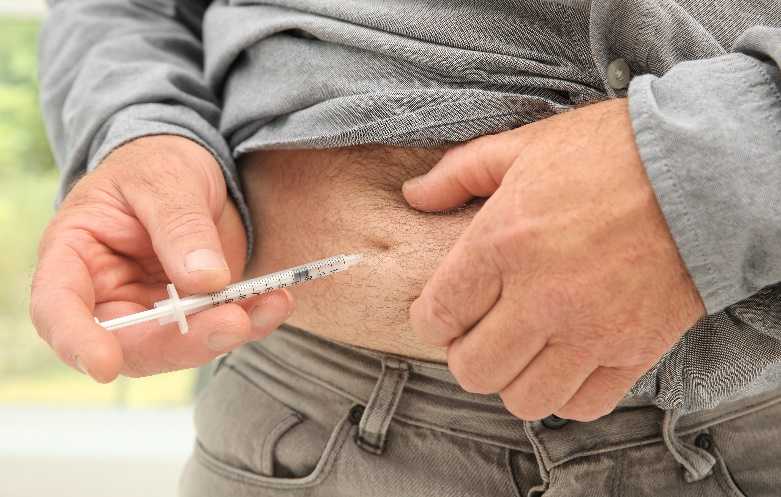
Aging naturally leads to a gradual decline in testosterone levels, but not all men will experience symptoms severe enough to warrant testosterone therapy. The safety and efficacy of testosterone therapy in older men depend on individual health profiles, pre-existing conditions, and specific symptoms of low testosterone.
Concerns about the safety of testosterone therapy in aging men primarily revolve around cardiovascular risks, prostate health, and the potential for other side effects. Some studies have suggested an increased risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes, in older men undergoing testosterone therapy, especially those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions. However, other research has found no significant increase in cardiovascular risk, indicating the need for individual assessment and cautious monitoring.
Regarding prostate health, while testosterone therapy has historically been thought to exacerbate prostate cancer growth, recent evidence suggests that testosterone therapy does not significantly increase the risk of prostate cancer development in men with normal prostate cancer screening results before treatment. Nonetheless, regular monitoring of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels and prostate health is crucial for men on testosterone therapy.
Given these considerations, testosterone therapy can be safe for some aging men with symptomatic low testosterone levels, provided there is careful screening for contraindications, close monitoring for side effects, and ongoing evaluation of therapy efficacy. Decisions about testosterone therapy should always be made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the potential benefits and risks for each individual.
While testosterone therapy offers potential benefits for erectile dysfunction and aging-related symptoms of low testosterone, it requires a nuanced approach that considers individual patient factors and involves careful monitoring to ensure safety and effectiveness.
How does testosterone therapy compare to other forms of treatment?
When considering the treatment of low testosterone or hypogonadism, testosterone therapy can be administered through various modalities, including injections, patches, gels, and even oral medications. Each method has its unique advantages, side effects, and implications for patient lifestyle and preference.
Testosterone Injections are highly effective in rapidly increasing testosterone levels and are typically administered every two to four weeks. This method ensures direct absorption into the bloodstream, providing a more controlled dosage and often a quicker response in symptom relief. However, the need for regular injections may be seen as inconvenient by some, and fluctuations in testosterone levels can lead to varying mood and energy levels.
Testosterone Gels and Patches offer a non-invasive alternative, applied daily to the skin, allowing for a more steady release of testosterone. This can help maintain more consistent testosterone levels, potentially reducing mood swings associated with the injection's peak and trough effect. However, there's a risk of transference to others through skin contact, and some patients may experience skin irritation or allergic reactions at the application site.
Oral Testosterone is less commonly used due to concerns over liver toxicity and the need for frequent dosing. However, new formulations are being developed that might mitigate these risks, offering more convenience than traditional injections or transdermal options.
Comparatively, while injections might provide a more immediate and controllable adjustment of testosterone levels, gels and patches offer the convenience of daily use with a more stable hormone level. The choice between these treatments depends on individual patient factors, including specific symptoms, lifestyle preferences, potential side effects, and cost considerations.
In addition to these direct testosterone replacement options, other treatments may address symptoms of low testosterone or contribute to its management. Lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, have been shown to positively affect testosterone levels and overall health. Furthermore, medications that stimulate the body's testosterone production, such as clomiphene citrate, may be suitable for some patients, particularly those concerned about fertility.
Can lifestyle changes impact the effectiveness of testosterone therapy?
Lifestyle factors play a crucial role in managing low testosterone levels and can significantly impact the effectiveness of testosterone therapy. Positive lifestyle changes can complement the benefits of testosterone therapy, potentially enhancing its outcomes and improving overall health.
Diet and Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in key nutrients can support testosterone production. Foods high in zinc, magnesium, and vitamin D have been linked to higher testosterone levels. Reducing excessive sugar and processed foods can also help manage weight and reduce the risk of conditions that may exacerbate low testosterone, such as type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Exercise: Regular physical activity, especially strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT), has been shown to boost testosterone levels naturally. Exercise not only helps in increasing muscle mass and reducing fat but also improves cardiovascular health, mood, and energy levels.
Stress Management: Chronic stress leads to elevated levels of cortisol, a hormone that negatively affects testosterone production. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, adequate sleep, and relaxation exercises can help reduce stress and its impact on testosterone levels.
Limiting Alcohol and Smoking: Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking have been linked to lower testosterone levels. Reducing or eliminating these habits can improve not only testosterone levels but also overall health and the effectiveness of testosterone therapy.
Sleep Quality: Adequate sleep is vital for testosterone production. Poor sleep patterns can significantly reduce testosterone levels. Ensuring 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night can help optimize hormone levels and enhance the benefits of testosterone therapy.
While testosterone therapy can directly address symptoms of low testosterone, integrating lifestyle changes can significantly enhance the therapy's effectiveness. Patients are encouraged to adopt a holistic approach that combines medical treatment with healthy lifestyle modifications to achieve the best outcomes in managing low testosterone levels.
Conclusion
The journey through the intricacies of testosterone therapy shots reveals a nuanced landscape of benefits, risks, and individual considerations. As we have explored, testosterone therapy offers a beacon of hope for men grappling with the physical and psychological burdens of low testosterone levels. From enhancing sexual function and mood to improving muscle mass and bone density, the potential benefits paint a compelling picture of transformation.
Yet, this journey is not without its cautionary paths. The risks and side effects associated with testosterone therapy — ranging from cardiovascular concerns to the potential impacts on prostate health — remind us of the critical importance of careful, personalized medical guidance. The decision to embark on testosterone therapy should never be taken lightly, nor should it be seen as a one-size-fits-all solution. It requires a thoughtful assessment of each individual's health profile, needs, and life circumstances.
Moreover, the exploration of alternative treatments and the impactful role of lifestyle changes highlight the multifaceted approach to managing low testosterone levels. Diet, exercise, stress management, and the avoidance of harmful habits work in concert with medical interventions to support overall health and wellbeing.
As we conclude, it's evident that the narrative of testosterone therapy is complex and evolving. Ongoing research and clinical practice continue to shed light on how best to harness the benefits of testosterone therapy while minimizing its risks. For those considering or currently undergoing testosterone therapy, this underscores the importance of an informed, proactive partnership with healthcare providers.
In navigating the path of testosterone therapy, let the guiding principles be knowledge, caution, and personalized care. With these as our compass, the journey toward improved health and quality of life, for those affected by low testosterone levels, can be undertaken with confidence and hope.
Questions and Answers